Menus and toolbars in PyQt6
last modified January 10, 2023
In this part of the PyQt6 tutorial, we create a statusbar, menubar and a toolbar. A menu is a group of commands located in a menubar. A toolbar has buttons with some common commands in the application. Statusbar shows status information, usually at the bottom of the application window.
PyQt6 QMainWindow
The QMainWindow class provides a main application window. This
enables to create a classic application skeleton with a statusbar, toolbars, and
a menubar.
PyQt6 statusbar
A statusbar is a widget that is used for displaying status information.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a statusbar.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.statusBar().showMessage('Ready')
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Statusbar')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The statusbar is created with the help of the QMainWindow widget.
self.statusBar().showMessage('Ready')
To get the statusbar, we call the statusBar method of the
QMainWindow class. The first call of the method creates a
status bar. Subsequent calls return the statusbar object. The
showMessage displays a message on the statusbar.
PyQt6 simple menu
A menubar is a common part of a GUI application. It is a group of commands
located in various menus. (Mac OS treats menubars differently. To get
a similar outcome, we can add the following line:
menubar.setNativeMenuBar(False).)
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a menubar. The
menubar has one menu with an exit action.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
exitAct = QAction(QIcon('exit.png'), '&Exit', self)
exitAct.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q')
exitAct.setStatusTip('Exit application')
exitAct.triggered.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
self.statusBar()
menubar = self.menuBar()
fileMenu = menubar.addMenu('&File')
fileMenu.addAction(exitAct)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Simple menu')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In the above example, we create a menubar with one menu. This menu contains one action which terminates the application if selected. A statusbar is created as well. The action is accessible with the Ctrl+Q shortcut.
exitAct = QAction(QIcon('exit.png'), '&Exit', self)
exitAct.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q')
exitAct.setStatusTip('Exit application')
QAction is an abstraction for actions
performed with a menubar, toolbar, or with a custom keyboard shortcut.
In the above three lines, we create an action with a specific icon and
an 'Exit' label. Furthermore, a shortcut is defined for this action.
The third line creates a status tip which is shown in the statusbar when
we hover a mouse pointer over the menu item.
exitAct.triggered.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
When we select this particular action, a triggered signal is emitted.
The signal is connected to the quit method of the
QApplication widget. This terminates the application.
menubar = self.menuBar()
fileMenu = menubar.addMenu('&File')
fileMenu.addAction(exitAction)
The menuBar method creates a menubar. We create a file menu with
addMenu and add the action with addAction.
PyQt6 submenu
A submenu is a menu located inside another menu.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a submenu.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QMenu, QApplication
from PyQt6.QtGui import QAction
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
menubar = self.menuBar()
fileMenu = menubar.addMenu('File')
impMenu = QMenu('Import', self)
impAct = QAction('Import mail', self)
impMenu.addAction(impAct)
newAct = QAction('New', self)
fileMenu.addAction(newAct)
fileMenu.addMenu(impMenu)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Submenu')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
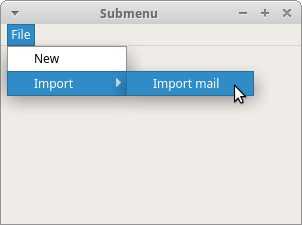
In the example, we have two menu items; one is located in the File menu and the other one in the File's Import submenu.
impMenu = QMenu('Import', self)
New menu is created with QMenu.
impAct = QAction('Import mail', self)
impMenu.addAction(impAct)
An action is added to the submenu with addAction.
PyQt6 check menu
In the following example, we create a menu that can be checked and unchecked.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a checkable menu.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt6.QtGui import QAction
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.statusbar = self.statusBar()
self.statusbar.showMessage('Ready')
menubar = self.menuBar()
viewMenu = menubar.addMenu('View')
viewStatAct = QAction('View statusbar', self, checkable=True)
viewStatAct.setStatusTip('View statusbar')
viewStatAct.setChecked(True)
viewStatAct.triggered.connect(self.toggleMenu)
viewMenu.addAction(viewStatAct)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Check menu')
self.show()
def toggleMenu(self, state):
if state:
self.statusbar.show()
else:
self.statusbar.hide()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
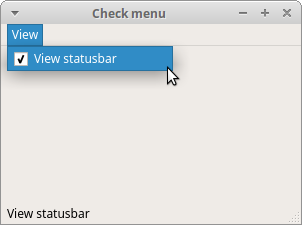
The code example creates a View menu with one action. The action shows or hides a statusbar. When the statusbar is visible, the menu item is checked.
viewStatAct = QAction('View statusbar', self, checkable=True)
With the checkable option we create a checkable menu.
viewStatAct.setChecked(True)
Since the statusbar is visible from the start, we check the action with
setChecked method.
def toggleMenu(self, state):
if state:
self.statusbar.show()
else:
self.statusbar.hide()
Depending on the state of the action, we show or hide the statusbar.
PyQt6 context menu
A context menu, also called a popup menu, is a list of commands that appears under some context. For example, in a Opera web browser when we right click on a web page, we get a context menu. Here we can reload a page, go back, or view a page source. If we right click on a toolbar, we get another context menu for managing toolbars.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a context menu.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QMenu, QApplication
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Context menu')
self.show()
def contextMenuEvent(self, event):
cmenu = QMenu(self)
newAct = cmenu.addAction("New")
openAct = cmenu.addAction("Open")
quitAct = cmenu.addAction("Quit")
action = cmenu.exec(self.mapToGlobal(event.pos()))
if action == quitAct:
QApplication.instance().quit()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
To work with a context menu, we have to reimplement the
contextMenuEvent method.
action = cmenu.exec(self.mapToGlobal(event.pos()))
The context menu is displayed with the exec method. The get the
coordinates of the mouse pointer from the event object. The
mapToGlobal method translates the widget coordinates to the global
screen coordinates.
if action == quitAct:
QApplication.instance().quit()
If the action returned from the context menu equals to quit action, we terminate the application.
PyQt6 toolbar
Menus group all commands that we can use in an application. Toolbars provide a quick access to the most frequently used commands.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a toolbar.
The toolbar has one action, which
terminates the application, if triggered.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
exitAct = QAction(QIcon('exit24.png'), 'Exit', self)
exitAct.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q')
exitAct.triggered.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
self.toolbar = self.addToolBar('Exit')
self.toolbar.addAction(exitAct)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Toolbar')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
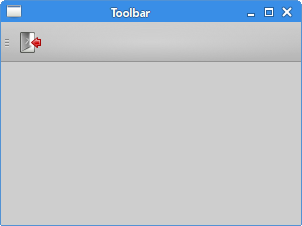
In the above example, we create a simple toolbar. The toolbar has one tool action, an exit action which terminates the application when triggered.
exitAct = QAction(QIcon('exit24.png'), 'Exit', self)
exitAct.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q')
exitAct.triggered.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
Similar to the menubar example above, we create an action object.
The object has a label, icon, and a shorcut. A quit method of the
QApplication is connected to the triggered signal.
self.toolbar = self.addToolBar('Exit')
self.toolbar.addAction(exitAction)
The toolbar is created with the addToolBar method. We add an action
object to the toolbar with addAction.
PyQt6 main window
In the last example of this section, we create a menubar, toolbar, and a statusbar. We also create a central widget.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt6 tutorial
This program creates a skeleton of
a classic GUI application with a menubar,
toolbar, statusbar, and a central widget.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QTextEdit, QApplication
from PyQt6.QtGui import QIcon, QAction
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
textEdit = QTextEdit()
self.setCentralWidget(textEdit)
exitAct = QAction(QIcon('exit24.png'), 'Exit', self)
exitAct.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q')
exitAct.setStatusTip('Exit application')
exitAct.triggered.connect(self.close)
self.statusBar()
menubar = self.menuBar()
fileMenu = menubar.addMenu('&File')
fileMenu.addAction(exitAct)
toolbar = self.addToolBar('Exit')
toolbar.addAction(exitAct)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Main window')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
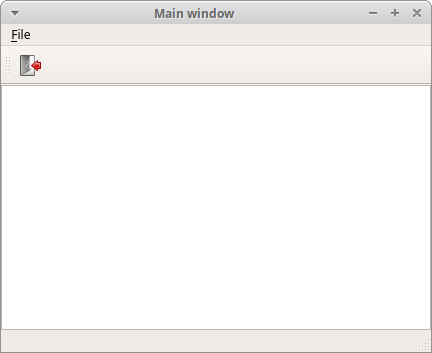
This code example creates a skeleton of a classic GUI application with a menubar, toolbar, and a statusbar.
textEdit = QTextEdit() self.setCentralWidget(textEdit)
Here we create a text edit widget. We set it to be the central widget of the
QMainWindow. The central widget occupies all space that is left.
In this part of the PyQt6 tutorial, we worked with menus, toolbars, a statusbar, and a main application window.