PyQt QRadioButton
last modified August 24, 2023
In this article we show how to work with QRadioButton widget.
Visit Advanced PyQt5 e-book, read PyQt6 tutorial, or list all PyQt tutorials.
QRadioButton
QRadioButton is a button that is turned on or off. Radio buttons
present multiple choices. In a group of radio buttons, only one radio button at
a time can be checked; if the user selects another button, the previously
selected button is turned off.
Radio buttons are auto-exclusive by default. If we want to have multiple
separated groups of radio buttons, we put them into QButtonGroup.
Whenever a button is turned on or off, it emits the toggled signal.
toggled signals are emitted.
PyQt QRadioButton example
The following is a simple example that uses QRadioButtons.
#!/usr/bin/python
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QRadioButton, QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout,
QLabel, QApplication)
import sys
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
hbox = QHBoxLayout()
rb1 = QRadioButton("Large", self)
rb1.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel)
rb2 = QRadioButton("Middle", self)
rb2.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel)
rb3 = QRadioButton("Small", self)
rb3.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel)
self.label = QLabel('', self)
hbox.addWidget(rb1)
hbox.addWidget(rb2)
hbox.addWidget(rb3)
vbox.addSpacing(15)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
vbox.addWidget(self.label)
self.setLayout(vbox)
self.setGeometry(400, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('QRadioButton')
self.show()
def updateLabel(self, _):
rbtn = self.sender()
if rbtn.isChecked() == True:
self.label.setText(rbtn.text())
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
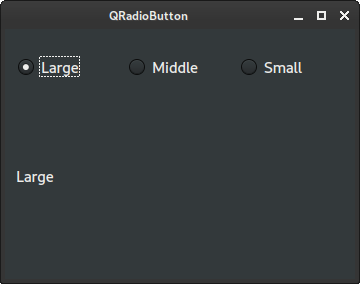
We have three radio buttons. Only one button can be selected at a time. The text of the selected radio button is displayed in the adjacent label.
rb1 = QRadioButton("Large", self)
A QRadioButton is created. The first parameter is its text label.
rb1.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel)
When we click on the radio button, the toggled signal is emitted.
def updateLabel(self, _):
rbtn = self.sender()
if rbtn.isChecked() == True:
self.label.setText(rbtn.text())
In the updateLabel handler, we determine the widget that invoked
it with sender. The isChecked function checks if
the radio button is turned on. If it is, we update the label with its text.
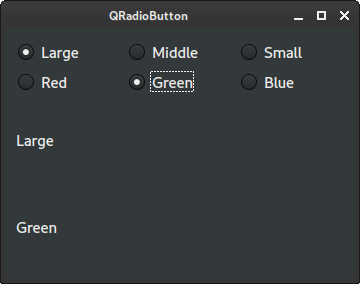
QRadioButton in QButtonGroup
The QButtonGroup class provides a container to organize groups of
button widgets.
#!/usr/bin/python
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QRadioButton, QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout,
QButtonGroup, QLabel, QApplication)
import sys
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
hbox1 = QHBoxLayout()
bg1 = QButtonGroup(self)
rb1 = QRadioButton('Large', self)
rb1.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel1)
rb2 = QRadioButton('Middle', self)
rb2.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel1)
rb3 = QRadioButton('Small', self)
rb3.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel1)
hbox2 = QHBoxLayout()
bg2 = QButtonGroup(self)
rb4 = QRadioButton('Red', self)
rb4.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel2)
rb5 = QRadioButton('Green', self)
rb5.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel2)
rb6 = QRadioButton('Blue', self)
rb6.toggled.connect(self.updateLabel2)
self.label1 = QLabel('', self)
self.label2 = QLabel('', self)
bg1.addButton(rb1)
bg1.addButton(rb2)
bg1.addButton(rb3)
bg2.addButton(rb4)
bg2.addButton(rb5)
bg2.addButton(rb6)
hbox1.addWidget(rb1)
hbox1.addWidget(rb2)
hbox1.addWidget(rb3)
hbox2.addWidget(rb4)
hbox2.addWidget(rb5)
hbox2.addWidget(rb6)
vbox.addLayout(hbox1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox2)
vbox.addWidget(self.label1)
vbox.addWidget(self.label2)
self.setLayout(vbox)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('QRadioButton')
self.show()
def updateLabel1(self, _):
rbtn = self.sender()
if rbtn.isChecked() == True:
self.label1.setText(rbtn.text())
def updateLabel2(self, _):
rbtn = self.sender()
if rbtn.isChecked() == True:
self.label2.setText(rbtn.text())
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In the example, we have two groups of radio buttons. To separate them, we place
them into two QButtonGroups.
bg1 = QButtonGroup(self)
A QButtonGroup is created. It is a container widget used to manage
buttons. It does not provide any visual representation.
bg1.addButton(rb1) bg1.addButton(rb2) bg1.addButton(rb3) bg2.addButton(rb4) bg2.addButton(rb5) bg2.addButton(rb6)
The buttons are put into the button group with addButton function.
In this article we have worked with PyQt QRadioButton.
Author
List all PyQt tutorials.