Java validation filter
last modified January 27, 2024
In this article we show how to validate data entered by the user in a web application. Validation is a common task and is covered in Java web frameworks such as Stripes, Ninja framework, or Play framework. In this article we will validate data with a simple custom validation filter. The sources are available at the author's Github repository.
A filter is an object that performs filtering tasks on either the request to a resource,
or on the response from a resource, or both. Filters perform filtering in the
doFilter method.
Filters can be used for various tasks such as authentication, logging, data compression, image conversion, or encryption. In our example, we use a filter to validate input data.
In our application, we have a HTML form that takes input from a user. The form has two input tags: user name and email. The input is being validated with a filter. To validate the email format, we use the Apache Commons Validator. The project is built with Maven in NetBeans IDE. We deploy the application on Tomcat.
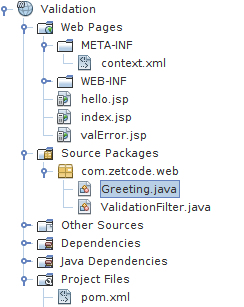
The figure shows the project structure in NetBeans. We have three JSP pages, two Java classes, and two XML configuration files.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zetcode</groupId>
<artifactId>Validation</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Validation</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax</groupId>
<artifactId>javaee-web-api</artifactId>
<version>7.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-validator</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-validator</artifactId>
<version>1.5.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArguments>
<endorseddirs>${endorsed.dir}</endorseddirs>
</compilerArguments>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
This is the pom.xml build file. It contains dependencies for
dependencies for JSTL and Apache Commons Validator.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Context path="/Validation"/>
In the context.xml file we specify the context path for
the application. It is used to uniquely identify the application.
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Validation</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Enter your name and email:
</p>
<form method="post" action="Greet">
Name: <input type="text" name="username"> <br>
Email: <input type="text" name="email"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
The index.jsp is the entry point of the application. It has
a HTML form with two fields. The values entered into these fields will
be validated by the application.
<form method="post" action="Greet"> ... </form>
Upon submitting the form, the Greet servlet is invoked.
Before reaching the servlet, a filter will process the request.
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Greeting</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello <c:out value="${param.username}"/>! <br>
Your email is <c:out value="${param.email}"/>.
</body>
</html>
When the input data passes the validation test, the hello.jsp page
is displayed. It shows the entered data.
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<c:out value="${errMsg}"/>
</p>
</body>
</html>
If the validation fails, the valError.jsp is displayed. It shows
the error message stored in the errMsg attribute. The attribute
is set in the validation filter.
package com.zetcode.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import org.apache.commons.validator.routines.EmailValidator;
@WebFilter(filterName = "ValidationFilter", urlPatterns = {"/Greet"})
public class ValidationFilter implements Filter {
public ValidationFilter() { }
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
String erpg = "valError.jsp";
String userName = request.getParameter("username");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
boolean valid = EmailValidator.getInstance().isValid(email);
if (userName == null || "".equals(userName)
|| email == null || "".equals(email)) {
request.setAttribute("errMsg", "One or both fields are empty");
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(erpg);
rd.include(request, response);
} else if (!valid) {
request.setAttribute("errMsg", "Email format not valid");
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(erpg);
rd.include(request, response);
} else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() { }
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) { }
}
The validation of data is performed in the ValidationFilter class.
@WebFilter(filterName = "ValidationFilter", urlPatterns = {"/Greet"})
The @WebFilter annotation declares a servlet filter.
The filter is applied on the specified URL pattern. In our case, it is
invoked before the invocation of the Greet servlet.
public class ValidationFilter implements Filter {
A filter implements the Filter interface.
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
...
}
The actual work is done in the doFilter method.
String userName = request.getParameter("username");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
With the getParameter method, we get the data sent
by the HTML form.
boolean valid = EmailValidator.getInstance().isValid(email);
Using the Apache Commons Validator's EmailValidator we
check the validity of the email format.
if (userName == null || "".equals(userName)
|| email == null || "".equals(email)) {
request.setAttribute("errMsg", "One or both fields are empty");
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(erpg);
rd.include(request, response);
} else if (!valid) {
request.setAttribute("errMsg", "Email format not valid");
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher(erpg);
rd.include(request, response);
} else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
If the data fails to validate, the processing is dispatched to the
error page with the RequestDispatcher. Otherwise, the
request continues its trip to the destination servlet.
package com.zetcode.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(name = "Greeting", urlPatterns = {"/Greet"})
public class Greeting extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
String page = "/hello.jsp";
RequestDispatcher disp = getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher(page);
disp.forward(request, response);
}
}
The Greeting servlet simply dispatches the request to the hello.jsp page
with the RequestDispatcher.
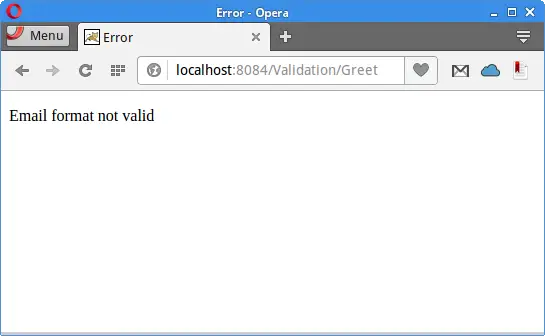
The application responds with an error message if the email has an incorrect format.
This was the validation filter tutorial. We have built a web application using JSTL, JSP, Apache Commons Validator, Tomcat, and Maven.
Source
Author
List all Java tutorials.