Windows API controls III
last modified October 18, 2023
In this chapter, we finish talking about Windows API controls. We mention radio buttons, radio box, combo box, and a progress bar.
Radio buttons and GroupBox
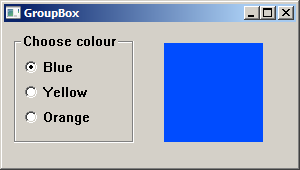
Here we introduce two controls. A group box is a rectangle that surrounds a set of controls. These are often radio buttons. A group box has a label that describes the control. The purpose of this control is to group controls that are somehow related. A radio button is a special kind of button that can be selected by the user, but not cleared. It allows the user to select a single exclusive choice from a group of options.
#include <windows.h>
#define ID_BLUE 1
#define ID_YELLOW 2
#define ID_ORANGE 3
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
HINSTANCE g_hinst;
COLORREF g_color;
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
PWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow) {
HWND hwnd;
MSG msg ;
WNDCLASSW wc = {0};
wc.lpszClassName = L"GroupBox";
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hbrBackground = GetSysColorBrush(COLOR_3DFACE);
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(0, IDC_ARROW);
g_hinst = hInstance;
RegisterClassW(&wc);
hwnd = CreateWindowW(wc.lpszClassName, L"GroupBox",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE,
100, 100, 300, 170, 0, 0, hInstance, 0);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) {
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return (int) msg.wParam;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
HDC hdc;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HBRUSH hBrush, holdBrush;
HPEN hPen, holdPen;
switch(msg) {
case WM_CREATE:
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Choose colour",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_GROUPBOX,
10, 10, 120, 110, hwnd, (HMENU) 0, g_hinst, NULL);
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Blue",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_AUTORADIOBUTTON,
20, 30, 100, 30, hwnd, (HMENU) ID_BLUE , g_hinst, NULL);
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Yellow",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_AUTORADIOBUTTON,
20, 55, 100, 30, hwnd, (HMENU) ID_YELLOW , g_hinst, NULL);
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Orange",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_AUTORADIOBUTTON,
20, 80, 100, 30, hwnd, (HMENU) ID_ORANGE , g_hinst, NULL);
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (HIWORD(wParam) == BN_CLICKED) {
switch (LOWORD(wParam)) {
case ID_BLUE:
g_color = RGB(0, 76, 255);
break;
case ID_YELLOW:
g_color = RGB(255, 255, 0);
break;
case ID_ORANGE:
g_color = RGB(255, 123, 0);
break;
}
InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, TRUE);
}
break;
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps);
hBrush = CreateSolidBrush(g_color);
hPen = CreatePen(PS_NULL, 1, RGB(0, 0, 0));
holdPen = SelectObject(hdc, hPen);
holdBrush = (HBRUSH) SelectObject(hdc, hBrush);
Rectangle(hdc, 160, 20, 260, 120);
SelectObject(hdc, holdBrush);
SelectObject(hdc, holdPen);
DeleteObject(hPen);
DeleteObject(hBrush);
EndPaint(hwnd, &ps);
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
}
return DefWindowProcW(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
In our example, we have a group box with three radio buttons. By clicking on the radio button, we select a background colour for the rectangle on the right.
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Choose colour",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_GROUPBOX,
10, 10, 120, 110, hwnd, (HMENU) 0, g_hinst, NULL);
A group box is a special kind of a button created with the BS_GROUPBOX style.
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Blue",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | BS_AUTORADIOBUTTON,
20, 30, 100, 30, hwnd, (HMENU) ID_BLUE , g_hinst, NULL);
A radio button is also a special kind of a button with BS_AUTORADIOBUTTON style.
case ID_BLUE:
g_color = RGB(0, 76, 255);
break;
If we click on the radio button, a global variable is filled with selected colour. This variable is used to create a brush that fills the rectangle.
InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, TRUE);
We invalidate the rectangle (in this case whole window), which will cause the
client area to be redrawn. This will launch a WM_PAINT message.
During the WM_PAINT message, we draw the rectangle. Drawing is explained
in GDI chapter in more detail.
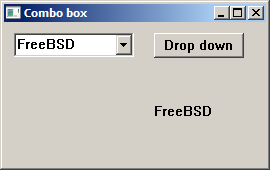
Combo box
A combo box is a combination of an edit box or static text and a list. A combo box is used when we need to select an item from a list of available options.
#include <windows.h>
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
HINSTANCE g_hinst;
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
PWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow) {
HWND hwnd;
MSG msg ;
WNDCLASSW wc = {0};
wc.lpszClassName = L"Application";
wc.hInstance = hInstance ;
wc.hbrBackground = GetSysColorBrush(COLOR_3DFACE);
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc ;
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(0,IDC_ARROW);
g_hinst = hInstance;
RegisterClassW(&wc);
hwnd = CreateWindowW(wc.lpszClassName, L"Combo box",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE,
100, 100, 270, 170, 0, 0, hInstance, 0);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) {
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return (int) msg.wParam;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
static HWND hwndCombo, hwndStatic;
const wchar_t *items[] = { L"FreeBSD", L"OpenBSD",
L"NetBSD", L"Solaris", L"Arch" };
switch(msg) {
case WM_CREATE:
hwndCombo = CreateWindowW(L"Combobox", NULL,
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | CBS_DROPDOWN,
10, 10, 120, 110, hwnd, NULL, g_hinst, NULL);
CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Drop down",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
150, 10, 90, 25, hwnd, (HMENU) 1, g_hinst, NULL);
hwndStatic = CreateWindowW(L"Static", L"",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
150, 80, 90, 25, hwnd, NULL, g_hinst, NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) {
SendMessageW(hwndCombo, CB_ADDSTRING, 0, (LPARAM) items[i]);
}
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (HIWORD(wParam) == BN_CLICKED) {
SendMessage(hwndCombo, CB_SHOWDROPDOWN, (WPARAM) TRUE, 0);
}
if (HIWORD(wParam) == CBN_SELCHANGE) {
LRESULT sel = SendMessage(hwndCombo, CB_GETCURSEL, 0, 0);
SetWindowTextW(hwndStatic, items[sel]);
}
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
}
return DefWindowProcW(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
In our example, we put three controls on the window: a combo box, a button, and
a static text. The static text displays the currently selected item from the
combo box. It is used to demonstrate the CBN_SELCHANGE combo box message.
The button programatically opens the combo box.
hwndCombo = CreateWindowW(L"Combobox", NULL,
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | CBS_DROPDOWN,
10, 10, 120, 110, hwnd, NULL, g_hinst, NULL);
To create a combo box, we use the L"Combobox" window class.
The CBS_DROPDOWN flag creates a drop-down list.
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) {
SendMessageW(hwndCombo, CB_ADDSTRING, 0, (LPARAM) items[i]);
}
We fill the combo box with items. To add a string to the combo box, we
send a CB_ADDSTRING message.
if (HIWORD(wParam) == BN_CLICKED) {
SendMessage(hwndCombo, CB_SHOWDROPDOWN, (WPARAM) TRUE, 0);
}
Clicking on the button causes a CB_SHOWDROPDOWN message to be send, which
programmatically invokes a drop down of the combo box.
If we select an item from the combo box, the window procedure receives the
WM_COMMAND message with the notification message CBN_SELCHANGE in the
high-order word of the wParam parameter.
if (HIWORD(wParam) == CBN_SELCHANGE) {
LRESULT sel = SendMessage(hwndCombo, CB_GETCURSEL, 0, 0);
SetWindowTextW(hwndStatic, items[sel]);
}
We figure out the currently selected item. We send a CB_GETCURSEL
message to the combo box. The function returns the index of the currently selected item.
We set the static text to the currently selected string.
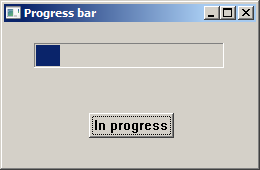
Progress bar
A progress bar is a control that is used when we process lengthy tasks. It is animated so that the user knows that our task is progressing.
#include <windows.h>
#include <commctrl.h>
#define ID_BUTTON 1
#define ID_TIMER 2
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND, UINT, WPARAM, LPARAM);
void CreateControls(HWND);
HWND hwndPrgBar;
HWND hbtn;
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
PWSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow) {
HWND hwnd;
MSG msg ;
WNDCLASSW wc = {0};
wc.lpszClassName = L"Application";
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hbrBackground = GetSysColorBrush(COLOR_3DFACE);
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(0, IDC_ARROW);
RegisterClassW(&wc);
hwnd = CreateWindowW(wc.lpszClassName, L"Progress bar",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE,
100, 100, 260, 170, 0, 0, hInstance, 0);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) {
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return (int) msg.wParam;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
static int i = 0;
switch(msg) {
case WM_CREATE:
CreateControls(hwnd);
break;
case WM_TIMER:
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_STEPIT, 0, 0);
i++;
if (i == 150) {
KillTimer(hwnd, ID_TIMER);
SendMessageW(hbtn, WM_SETTEXT, (WPARAM) NULL, (LPARAM) L"Start");
i = 0;
}
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (i == 0) {
i = 1;
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETPOS, 0, 0);
SetTimer(hwnd, ID_TIMER, 5, NULL);
SendMessageW(hbtn, WM_SETTEXT, (WPARAM) NULL, (LPARAM) L"In progress");
}
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
KillTimer(hwnd, ID_TIMER);
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
}
return DefWindowProcW(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
void CreateControls(HWND hwnd) {
INITCOMMONCONTROLSEX icex;
icex.dwSize = sizeof(INITCOMMONCONTROLSEX);
icex.dwICC = ICC_PROGRESS_CLASS;
InitCommonControlsEx(&icex);
hwndPrgBar = CreateWindowEx(0, PROGRESS_CLASS, NULL,
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | PBS_SMOOTH,
30, 20, 190, 25, hwnd, NULL, NULL, NULL);
hbtn = CreateWindowW(L"Button", L"Start",
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
85, 90, 85, 25, hwnd, (HMENU) 1, NULL, NULL);
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETRANGE, 0, MAKELPARAM(0, 150));
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETSTEP, 1, 0);
}
In our example, we have a progress bar and a button. The button starts a timer which updates the progress bar.
hwndPrgBar = CreateWindowEx(0, PROGRESS_CLASS, NULL,
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | PBS_SMOOTH,
30, 20, 190, 25, hwnd, NULL, NULL, NULL);
We create a progress bar control with PROGRESS_CLASS class name
and PBS_SMOOTH style.
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETRANGE, 0, MAKELPARAM(0, 150)); SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETSTEP, 1, 0);
We set the range of the progress bar and its step.
i = 1; SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_SETPOS, 0, 0); SetTimer(hwnd, ID_TIMER, 5, NULL);
When we press the Start button, we set the i value to 1, set the initial
position of the progress bar, and start the timer. The timer will
periodically send a WM_TIMER message to the window procedure,
until it is killed.
SendMessageW(hbtn, WM_SETTEXT, (WPARAM) NULL, (LPARAM) L"In progress");
When the timer is in progress, we change the label of the button.
case WM_TIMER:
SendMessage(hwndPrgBar, PBM_STEPIT, 0, 0);
i++;
if (i == 150) {
KillTimer(hwnd, ID_TIMER);
SendMessageW(hbtn, WM_SETTEXT, (WPARAM) NULL, (LPARAM) L"Start");
i = 0;
}
break;
When we receive the WM_TIMER message, we update the progress bar by one
step sending the PBM_STEPIT message. The timer is killed when the
i variable reaches the upper limit of the progress bar.
In this part of the Windows API tutorial, we have finished covering Windows controls.