Qt5 Widgets II
last modified October 18, 2023
In this part of the Qt5 C++ programming tutorial, we continue
talking about the Qt5 widgets. We cover the following widgets: QCheckBox,
QListWidget, QProgressBar, QPixmap,
QSplitter, and QTableWidget.
QCheckBox
The QCheckBox is a widget that has two states: on and off.
It is a box with a label. If the checkbox is checked, it is represented
by a tick in a box.
In our example, we display a checkbox on the window. If the checkbox is checked, the title of the window is displayed. Otherwise it is hidden.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class CheckBox : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
CheckBox(QWidget *parent = 0);
private slots:
void showTitle(int);
};
This is a header file for our code example.
#include <QCheckBox>
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include "checkbox.h"
CheckBox::CheckBox(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QCheckBox *cb = new QCheckBox("Show Title", this);
cb->setCheckState(Qt::Checked);
hbox->addWidget(cb, 0, Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop);
connect(cb, &QCheckBox::stateChanged, this, &CheckBox::showTitle);
}
void CheckBox::showTitle(int state) {
if (state == Qt::Checked) {
setWindowTitle("QCheckBox");
} else {
setWindowTitle(" ");
}
}
We display a checkbox on the window and connect it to the
showTitle slot.
cb->setCheckState(Qt::Checked);
The checkbox is checked when the example starts.
void CheckBox::showTitle(int state) {
if (state == Qt::Checked) {
setWindowTitle("QCheckBox");
} else {
setWindowTitle(" ");
}
}
We determine the state of the check box and call the setWindowTitle
accordingly.
#include <QApplication>
#include "checkbox.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
CheckBox window;
window.resize(250, 150);
window.setWindowTitle("QCheckBox");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
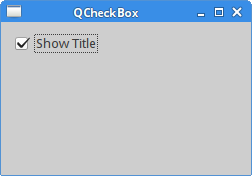
QListWidget
A QListWidget is a widget that is used to display a
list of items. In our example, we demonstrate how to add,
rename, and remove items from the list widget.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QListWidget>
class ListWidget : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
ListWidget(QWidget *parent = 0);
private slots:
void addItem();
void renameItem();
void removeItem();
void clearItems();
private:
QListWidget *lw;
QPushButton *add;
QPushButton *rename;
QPushButton *remove;
QPushButton *removeAll;
};
The header file for the example.
#include "listwidget.h"
#include <QVBoxLayout>
#include <QInputDialog>
ListWidget::ListWidget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QVBoxLayout *vbox = new QVBoxLayout();
vbox->setSpacing(10);
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
lw = new QListWidget(this);
lw->addItem("The Omen");
lw->addItem("The Exorcist");
lw->addItem("Notes on a scandal");
lw->addItem("Fargo");
lw->addItem("Capote");
add = new QPushButton("Add", this);
rename = new QPushButton("Rename", this);
remove = new QPushButton("Remove", this);
removeAll = new QPushButton("Remove All", this);
vbox->setSpacing(3);
vbox->addStretch(1);
vbox->addWidget(add);
vbox->addWidget(rename);
vbox->addWidget(remove);
vbox->addWidget(removeAll);
vbox->addStretch(1);
hbox->addWidget(lw);
hbox->addSpacing(15);
hbox->addLayout(vbox);
connect(add, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ListWidget::addItem);
connect(rename, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ListWidget::renameItem);
connect(remove, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ListWidget::removeItem);
connect(removeAll, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ListWidget::clearItems);
setLayout(hbox);
}
void ListWidget::addItem() {
QString c_text = QInputDialog::getText(this, "Item", "Enter new item");
QString s_text = c_text.simplified();
if (!s_text.isEmpty()) {
lw->addItem(s_text);
int r = lw->count() - 1;
lw->setCurrentRow(r);
}
}
void ListWidget::renameItem() {
QListWidgetItem *curitem = lw->currentItem();
int r = lw->row(curitem);
QString c_text = curitem->text();
QString r_text = QInputDialog::getText(this, "Item",
"Enter new item", QLineEdit::Normal, c_text);
QString s_text = r_text.simplified();
if (!s_text.isEmpty()) {
QListWidgetItem *item = lw->takeItem(r);
delete item;
lw->insertItem(r, s_text);
lw->setCurrentRow(r);
}
}
void ListWidget::removeItem() {
int r = lw->currentRow();
if (r != -1) {
QListWidgetItem *item = lw->takeItem(r);
delete item;
}
}
void ListWidget::clearItems(){
if (lw->count() != 0) {
lw->clear();
}
}
We display a list widget and four buttons. We use these buttons to add, rename, and remove items from the list widget.
lw = new QListWidget(this);
lw->addItem("The Omen");
lw->addItem("The Exorcist");
lw->addItem("Notes on a scandal");
lw->addItem("Fargo");
lw->addItem("Capote);
The QListWidget is created and filled with five items.
void ListWidget::addItem() {
QString c_text = QInputDialog::getText(this, "Item", "Enter new item");
QString s_text = c_text.simplified();
if (!s_text.isEmpty()) {
lw->addItem(s_text);
int r = lw->count() - 1;
lw->setCurrentRow(r);
}
}
The addItem method adds a new item to the list widget.
The method pops up an input dialog. The dialog returns a string value. We remove
possible white spaces from the string using the simplified method.
If the returned string is not empty, we add it to the list widget, at the end of the list.
Finally, we highlight the currently inserted item with the setCurrentRow
method.
void ListWidget::renameItem() {
QListWidgetItem *curitem = lw->currentItem();
int r = lw->row(curitem);
QString c_text = curitem->text();
QString r_text = QInputDialog::getText(this, "Item",
"Enter new item", QLineEdit::Normal, c_text);
QString s_text = r_text.simplified();
if (!s_text.isEmpty()) {
QListWidgetItem *item = lw->takeItem(r);
delete item;
lw->insertItem(r, s_text);
lw->setCurrentRow(r);
}
}
Renaming an item consists of several steps. First, we get the current item
using the currentItem method. We get the text of the
item and the row where the item is located. The text of the item
is displayed in the QInputDialog dialog. The string that
is returned from the dialog is processed by the simplified method
to remove potential white spaces. Then we remove the old item with
the takeItem method and replace it with the insertItem
method. We delete the item removed by the takeItem method, since
removed items are no longer managed by Qt. Finally, the setCurrentRow
selects the new item.
void ListWidget::removeItem() {
int r = lw->currentRow();
if (r != -1) {
QListWidgetItem *item = lw->takeItem(r);
delete item;
}
}
The removeItem removes a specific item from the list.
First, we get the currently selected row with the currentRow method.
(It returns -1 if there are no more rows left.) The currently selected item is
removed using the takeItem method.
void ListWidget::clearItems(){
if (lw->count() != 0) {
lw->clear();
}
}
The clear method removes all items from the
list widget.
#include <QApplication>
#include "listwidget.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
ListWidget window;
window.setWindowTitle("QListWidget");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
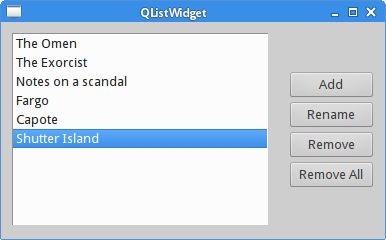
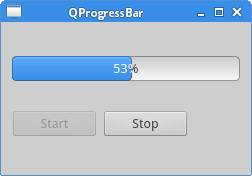
QProgressBar
QProgressBar is used to give the user an indication of the
progress of an operation.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
#include <QProgressBar>
#include <QPushButton>
class ProgressBarEx : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
ProgressBarEx(QWidget *parent = 0);
private:
int progress;
QTimer *timer;
QProgressBar *pbar;
QPushButton *startBtn;
QPushButton *stopBtn;
static const int DELAY = 200;
static const int MAX_VALUE = 100;
void updateBar();
void startMyTimer();
void stopMyTimer();
};
The header file for the example.
#include <QProgressBar>
#include <QTimer>
#include <QGridLayout>
#include "progressbar.h"
ProgressBarEx::ProgressBarEx(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
progress = 0;
timer = new QTimer(this);
connect(timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, &ProgressBarEx::updateBar);
QGridLayout *grid = new QGridLayout(this);
grid->setColumnStretch(2, 1);
pbar = new QProgressBar();
grid->addWidget(pbar, 0, 0, 1, 3);
startBtn = new QPushButton("Start", this);
connect(startBtn, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ProgressBarEx::startMyTimer);
grid->addWidget(startBtn, 1, 0, 1, 1);
stopBtn = new QPushButton("Stop", this);
connect(stopBtn, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &ProgressBarEx::stopMyTimer);
grid->addWidget(stopBtn, 1, 1);
}
void ProgressBarEx::startMyTimer() {
if (progress >= MAX_VALUE) {
progress = 0;
pbar->setValue(0);
}
if (!timer->isActive()) {
startBtn->setEnabled(false);
stopBtn->setEnabled(true);
timer->start(DELAY);
}
}
void ProgressBarEx::stopMyTimer() {
if (timer->isActive()) {
startBtn->setEnabled(true);
stopBtn->setEnabled(false);
timer->stop();
}
}
void ProgressBarEx::updateBar() {
progress++;
if (progress <= MAX_VALUE) {
pbar->setValue(progress);
} else {
timer->stop();
startBtn->setEnabled(true);
stopBtn->setEnabled(false);
}
}
In the example, we have a QProgressBar and two push buttons.
One button starts the timer, which in turn updates the progress bar.
The other button stops the timer.
timer = new QTimer(this); connect(timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, &ProgressBarEx::updateBar);
A QTimer is used to control the QProgressBar widget.
pbar = new QProgressBar();
An instance of a QProgressBar is created. The default minimum and
maximum values are 0 and 100.
if (!timer->isActive()) {
startBtn->setEnabled(false);
stopBtn->setEnabled(true);
timer->start(DELAY);
}
Depending on the state of the progress bar, the buttons are enabled or disabled.
This is accomplished with the setEnabled method.
void ProgressBarEx::updateBar() {
progress++;
if (progress <= MAX_VALUE) {
pbar->setValue(progress);
} else {
timer->stop();
startBtn->setEnabled(true);
stopBtn->setEnabled(false);
}
}
The progress is stored in the progress variable.
The setValue updates the current value of the progress bar.
#include <QApplication>
#include "progressbar.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
ProgressBarEx window;
window.resize(250, 150);
window.setWindowTitle("QProgressBar");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
QPixmap
QPixmap is one of the widgets used to work
with images. It is optimized for showing images on screen.
In our code example, we use QPixmap to
display an image on the window.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Pixmap : public QWidget {
public:
Pixmap(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
The header file for the example.
#include <QPixmap>
#include <QLabel>
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include "pixmap.h"
Pixmap::Pixmap(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QPixmap pixmap("bojnice.jpg");
QLabel *label = new QLabel(this);
label->setPixmap(pixmap);
hbox->addWidget(label, 0, Qt::AlignTop);
}
We show an image of a famous castle located in middle Slovakia.
QPixmap pixmap("bojnice.jpg");
QLabel *label = new QLabel(this);
label->setPixmap(pixmap);
We create a pixmap and put it inside a label widget.
#include <QApplication>
#include "pixmap.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Pixmap window;
window.setWindowTitle("QPixmap");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
QSplitter
QSplitter lets the user control the size of child
widgets by dragging the boundary between the children.
In our example, we show three QFrame widgets
organized with two splitters.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Splitter : public QWidget {
public:
Splitter(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
The header file for the example.
#include <QFrame>
#include <QSplitter>
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include "splitter.h"
Splitter::Splitter(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QFrame *topleft = new QFrame(this);
topleft->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
QFrame *topright = new QFrame(this);
topright->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
QSplitter *splitter1 = new QSplitter(Qt::Horizontal, this);
splitter1->addWidget(topleft);
splitter1->addWidget(topright);
QFrame *bottom = new QFrame(this);
bottom->setFrameShape(QFrame::StyledPanel);
QSplitter *splitter2 = new QSplitter(Qt::Vertical, this);
splitter2->addWidget(splitter1);
splitter2->addWidget(bottom);
QList<int> sizes({50, 100});
splitter2->setSizes(sizes);
hbox->addWidget(splitter2);
}
In the example, we have three frame widgets and two splitter widgets.
QSplitter *splitter1 = new QSplitter(Qt::Horizontal, this); splitter1->addWidget(topleft); splitter1->addWidget(topright);
We create a splitter widget and add two frame widgets into the splitter.
QSplitter *splitter2 = new QSplitter(Qt::Vertical, this); splitter2->addWidget(splitter1);
We can also add a splitter to another splitter widget.
QList<int> sizes({50, 100});
splitter2->setSizes(sizes);
With the setSizes method, we set the size for the splitter's
child widgets.
#include <QDesktopWidget>
#include <QApplication>
#include "splitter.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Splitter window;
window.resize(350, 300);
window.setWindowTitle("QSplitter");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
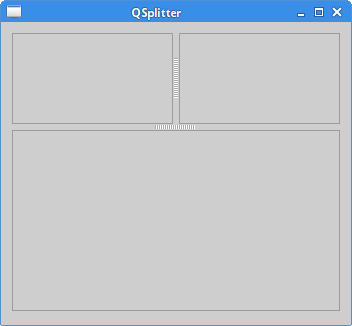
In some desktop themes, the splitter might be hard to see.
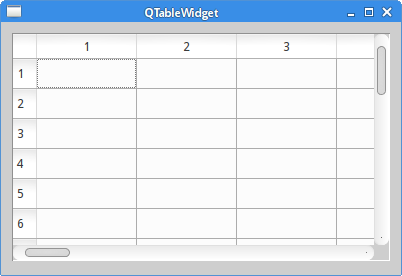
QTableWidget
QTableWidget is a unique widget used in
spreadsheet applications. (It is also called a grid widget).
It is one of the more complicated widgets. Here we only display
the widget on the window.
#pragma once
#include <QWidget>
class Table : public QWidget {
public:
Table(QWidget *parent = 0);
};
The header file for the example.
#include <QHBoxLayout>
#include <QTableWidget>
#include "table.h"
Table::Table(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) {
QHBoxLayout *hbox = new QHBoxLayout(this);
QTableWidget *table = new QTableWidget(25, 25, this);
hbox->addWidget(table);
}
The example shows a QTableWidget on the window.
QTableWidget *table = new QTableWidget(25, 25, this);
Here we create the table widget with 25 rows and 25 columns.
#include <QApplication>
#include "table.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Table window;
window.resize(400, 250);
window.setWindowTitle("QTableWidget");
window.show();
return app.exec();
}
This is the main file.
In this chapter, we have described several other Qt5 widgets.