Dialogs in PySide
last modified October 18, 2023
Dialog windows or dialogs are common in modern GUI applications. A dialog is defined as a conversation between two or more persons. In a computer application a dialog is a window which is used to "talk" to the application. A dialog is used to input data, modify data, change the application settings etc. Dialogs are important means of communication between a user and a computer program.
QtGui.QInputDialog
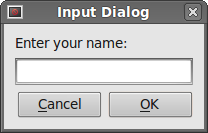
The QtGui.QInputDialog provides a simple convenience dialog
to get a single value from a user. The input value can be a string, a number,
or an item from a list.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
In this example, we receive data from
a QtGui.QInputDialog dialog.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.btn = QtGui.QPushButton('Dialog', self)
self.btn.move(20, 20)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.showDialog)
self.le = QtGui.QLineEdit(self)
self.le.move(130, 22)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 290, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Input dialog')
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
text, ok = QtGui.QInputDialog.getText(self, 'Input Dialog',
'Enter your name:')
if ok:
self.le.setText(str(text))
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The example has a button and a line edit widget. The button shows the input dialog for getting text values. The entered text will be displayed in the line edit widget.
text, ok = QtGui.QInputDialog.getText(self, 'Input Dialog',
'Enter your name:')
This line displays the input dialog. The first string is a dialog title, the second one is a message within the dialog. The dialog returns the entered text and a boolean value. If we clicked the ok button, the boolean value would be true, false otherwise.
if ok:
self.le.setText(str(text))
The text that we have received from the dialog is set to the line edit widget.
QtGui.QColorDialog
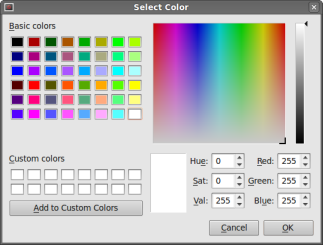
The QtGui.QColorDialog provides a dialog widget for
selecting colours.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
In this example, we select a colour value
from the QtGui.QColorDialog and change the background
colour of a QtGui.QFrame widget.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
col = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
self.btn = QtGui.QPushButton('Dialog', self)
self.btn.move(20, 20)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.showDialog)
self.frm = QtGui.QFrame(self)
self.frm.setStyleSheet("QWidget { background-color: %s }"
% col.name())
self.frm.setGeometry(130, 22, 100, 100)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 180)
self.setWindowTitle('Color dialog')
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
col = QtGui.QColorDialog.getColor()
if col.isValid():
self.frm.setStyleSheet("QWidget { background-color: %s }"
% col.name())
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The application example shows a push button and a QtGui.QFrame.
The widget background is set to black colour. Using the QtGui.QColorDialog,
we can change its background.
col = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
This is an initial colour of the QtGui.QFrame background.
col = QtGui.QColorDialog.getColor()
This line will pop up the QtGui.QColorDialog.
if col.isValid():
self.frm.setStyleSheet("QWidget { background-color: %s }"
% col.name())
We check if the colour is valid. If we click on the cancel button, no valid colour is returned. If the colour is valid, we change the background colour using style sheets.
QtGui.QFontDialog
The QtGui.QFontDialog is a dialog widget for selecting fonts.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
In this example, we select a font name
and change the font of a label.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout()
btn = QtGui.QPushButton('Dialog', self)
btn.setSizePolicy(QtGui.QSizePolicy.Fixed,
QtGui.QSizePolicy.Fixed)
btn.move(20, 20)
vbox.addWidget(btn)
btn.clicked.connect(self.showDialog)
self.lbl = QtGui.QLabel('Knowledge only matters', self)
self.lbl.move(130, 20)
vbox.addWidget(self.lbl)
self.setLayout(vbox)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 180)
self.setWindowTitle('Font dialog')
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
font, ok = QtGui.QFontDialog.getFont()
if ok:
self.lbl.setFont(font)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we have a button and a label. With QtGui.QFontDialog,
we change the font of the label.
font, ok = QtGui.QFontDialog.getFont()
Here we pop up the font dialog. The getFont method returns the
font name and the ok parameter. It is equal to True if the user clicked OK; otherwise
it is False.
if ok:
self.label.setFont(font)
If we clicked ok, the font of the label would be changed.
QtGui.QFileDialog
The QtGui.QFileDialog is a dialog that allows users to
select files or directories. The files can be selected for both
opening and saving.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
In this example, we select a file with a
QtGui.QFileDialog and display its contents
in a QtGui.QTextEdit.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.textEdit = QtGui.QTextEdit()
self.setCentralWidget(self.textEdit)
self.statusBar()
openFile = QtGui.QAction(QtGui.QIcon('open.png'), 'Open', self)
openFile.setShortcut('Ctrl+O')
openFile.setStatusTip('Open new File')
openFile.triggered.connect(self.showDialog)
menubar = self.menuBar()
fileMenu = menubar.addMenu('&File')
fileMenu.addAction(openFile)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 300)
self.setWindowTitle('File dialog')
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
fname, _ = QtGui.QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Open file',
'/home')
f = open(fname, 'r')
with f:
data = f.read()
self.textEdit.setText(data)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The example shows a menubar, centrally set text edit widget and a statusbar.
The the menu item shows the QtGui.QFileDialog
which is used to select a file. The contents of the file are loaded
into the text edit widget.
class Example(QtGui.QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
The example is based on the QtGui.QMainWindow widget.
We can easily create a statusbar, toolbar and a central widget.
fname, _ = QtGui.QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Open file',
'/home')
We pop up the QtGui.QFileDialog. The first string in
the getOpenFileName method is the caption. The second
string specifies the dialog working directory. The method returns
the selected file name and a filter. We are only interested in the file name.
f = open(fname, 'r')
with f:
data = f.read()
self.textEdit.setText(data)
The selected file name is read and the contents of the file are set to the text edit widget.
In this part of the PySide tutorial, we worked with dialogs.