Menus in PyGTK
last modified October 18, 2023
In this part of the PyGTK programming tutorial, we work with menus.
A menubar is one of the most common parts of the GUI application. It is a group of commands located in various menus. While in console applications you have to remember all those arcane commands, here we have most of the commands grouped into logical parts. These are accepted standards that further reduce the amount of time spent to learn a new application.
Simple menu
In our first example, we create a menubar with one file menu. The menu will have only one menu item. By selecting the item the application quits.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows a simple menu
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Simple menu")
self.set_size_request(250, 200)
self.modify_bg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, gtk.gdk.Color(6400, 6400, 6440))
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
mb = gtk.MenuBar()
filemenu = gtk.Menu()
filem = gtk.MenuItem("File")
filem.set_submenu(filemenu)
exit = gtk.MenuItem("Exit")
exit.connect("activate", gtk.main_quit)
filemenu.append(exit)
mb.append(filem)
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 2)
vbox.pack_start(mb, False, False, 0)
self.add(vbox)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
This is a small example with minimal menubar functionality.
mb = gtk.MenuBar()
MenuBar widget is created.
filemenu = gtk.Menu()
filem = gtk.MenuItem("File")
filem.set_submenu(filemenu)
Toplevel MenuItem is created.
exit = gtk.MenuItem("Exit")
exit.connect("activate", gtk.main_quit)
filemenu.append(exit)
Exit MenuItem is created and appended to the
File MenuItem.
mb.append(filem)
Toplevel MenuItem is appended to the MenuBar
widget.
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 2) vbox.pack_start(mb, False, False, 0)
Unlike in other toolkits, we have to take care of the layout management of the menubar ourselves. We put the menubar into a vertical box.
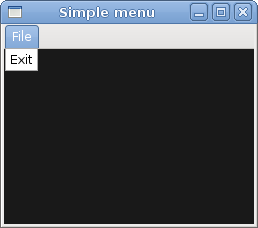
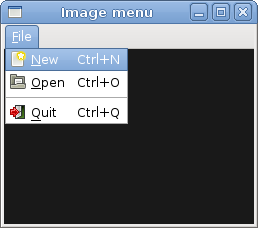
Image menu
In the next example, we further explore the menus. We add images and accelerators to our menu items. Accelerators are keyboard shortcuts for activating a menu item.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows a menu with
# images, accelerators and a separator
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Image menu")
self.set_size_request(250, 200)
self.modify_bg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, gtk.gdk.Color(6400, 6400, 6440))
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
mb = gtk.MenuBar()
filemenu = gtk.Menu()
filem = gtk.MenuItem("_File")
filem.set_submenu(filemenu)
agr = gtk.AccelGroup()
self.add_accel_group(agr)
newi = gtk.ImageMenuItem(gtk.STOCK_NEW, agr)
key, mod = gtk.accelerator_parse("<Control>N")
newi.add_accelerator("activate", agr, key,
mod, gtk.ACCEL_VISIBLE)
filemenu.append(newi)
openm = gtk.ImageMenuItem(gtk.STOCK_OPEN, agr)
key, mod = gtk.accelerator_parse("<Control>O")
openm.add_accelerator("activate", agr, key,
mod, gtk.ACCEL_VISIBLE)
filemenu.append(openm)
sep = gtk.SeparatorMenuItem()
filemenu.append(sep)
exit = gtk.ImageMenuItem(gtk.STOCK_QUIT, agr)
key, mod = gtk.accelerator_parse("<Control>Q")
exit.add_accelerator("activate", agr, key,
mod, gtk.ACCEL_VISIBLE)
exit.connect("activate", gtk.main_quit)
filemenu.append(exit)
mb.append(filem)
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 2)
vbox.pack_start(mb, False, False, 0)
self.add(vbox)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
Our example shows a toplevel menu item with three sublevel menu items. Each of the menu items has a image and an accelerator. The accelerator for the quit menu item is active.
agr = gtk.AccelGroup() self.add_accel_group(agr)
To work with accelerators, we create a global AccelGroup
object. It will be used later.
newi = gtk.ImageMenuItem(gtk.STOCK_NEW, agr)
ImageMenuItem is created. The image comes from the stock
of images.
key, mod = gtk.accelerator_parse("<Control>N")
The gtk.accelerator_parse function parses the specified
accelerator string and returns a 2-tuple containing the keyval
and modifier mask corresponding to accelerator.
newi.add_accelerator("activate", agr, key,
mod, gtk.ACCEL_VISIBLE)
This creates an Ctrl+Q accelerator for the exit menu item.
sep = gtk.SeparatorMenuItem() filemenu.append(sep)
These lines create a separator. It is used to group menu items into logical groups.
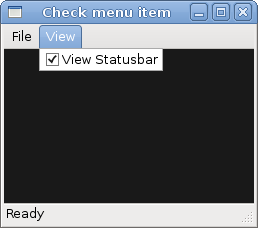
CheckMenuItem
A CheckMenuItem is a menu item with a check box.
It can be used to work with boolean properties.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows how to
# use a CheckMenuItem
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Check menu item")
self.set_size_request(250, 200)
self.modify_bg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, gtk.gdk.Color(6400, 6400, 6440))
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
mb = gtk.MenuBar()
filemenu = gtk.Menu()
filem = gtk.MenuItem("File")
filem.set_submenu(filemenu)
viewmenu = gtk.Menu()
view = gtk.MenuItem("View")
view.set_submenu(viewmenu)
stat = gtk.CheckMenuItem("View Statusbar")
stat.set_active(True)
stat.connect("activate", self.on_status_view)
viewmenu.append(stat)
exit = gtk.MenuItem("Exit")
exit.connect("activate", gtk.main_quit)
filemenu.append(exit)
mb.append(filem)
mb.append(view)
self.statusbar = gtk.Statusbar()
self.statusbar.push(1, "Ready")
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 2)
vbox.pack_start(mb, False, False, 0)
vbox.pack_start(gtk.Label(), True, False, 0)
vbox.pack_start(self.statusbar, False, False, 0)
self.add(vbox)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def on_status_view(self, widget):
if widget.active:
self.statusbar.show()
else:
self.statusbar.hide()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
In our code example we show a check menu item. If the check box is activated, the statusbar widget is shown. If not, the statusbar is hidden.
stat = gtk.CheckMenuItem("View Statusbar")
CheckMenuItem widget is created.
stat.set_active(True)
The set_active method checks/unchecks the
check menu item.
if widget.active:
self.statusbar.show()
else:
self.statusbar.hide()
Depending on the active property of the CheckMenuItem,
we show or hide the statusbar widget.
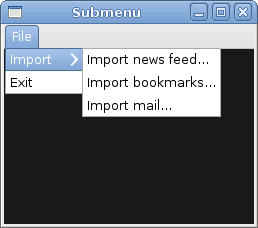
Submenu
Our final example demonstrates how to create a submenu in PyGTK.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows a submenu
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Submenu")
self.set_size_request(250, 200)
self.modify_bg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, gtk.gdk.Color(6400, 6400, 6440))
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
mb = gtk.MenuBar()
filemenu = gtk.Menu()
filem = gtk.MenuItem("File")
filem.set_submenu(filemenu)
mb.append(filem)
imenu = gtk.Menu()
importm = gtk.MenuItem("Import")
importm.set_submenu(imenu)
inews = gtk.MenuItem("Import news feed...")
ibookmarks = gtk.MenuItem("Import bookmarks...")
imail = gtk.MenuItem("Import mail...")
imenu.append(inews)
imenu.append(ibookmarks)
imenu.append(imail)
filemenu.append(importm)
exit = gtk.MenuItem("Exit")
exit.connect("activate", gtk.main_quit)
filemenu.append(exit)
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 2)
vbox.pack_start(mb, False, False, 0)
self.add(vbox)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
Submenu creation.
imenu = gtk.Menu()
A submenu is a Menu.
importm = gtk.MenuItem("Import")
importm.set_submenu(imenu)
It is a submenu of a menu item, which belogs to toplevel file menu.
inews = gtk.MenuItem("Import news feed...")
ibookmarks = gtk.MenuItem("Import bookmarks...")
imail = gtk.MenuItem("Import mail...")
imenu.append(inews)
imenu.append(ibookmarks)
imenu.append(imail)
Submenu has its own menu items.
In this chapter of the PyGTK programming library, we showed, how to work with menus.