Go Excel
last modified April 11, 2024
In this article we show how to read/write Excel files in Golang with excelize.
Excel xlsx
In this article we work with xlsx files. The xlsx is a file extension for an open XML spreadsheet file format used by Microsoft Excel. The xlsm files support macros. The xltm are macro-enabled template files. The xls format is a proprietary binary format while xlsx is based on Office Open XML format.
Go Excelize
Excelize is a Go library for reading and writing Excel files. It
supports xlsx, xlsm, and xltm files. Excelize allows to work with spreadsheet
documents generated by Microsoft Excel™ 2007 and later. It provides streaming
API for generating or reading data from a worksheet with huge amounts of data.
$ go get github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2
To install Excelize which supports modules, we use the above command.
Go Excel simple example
In the first example, we create a new xlsx file with excelize.
$ mkdir simple $ cd simple
We create a project directory.
$ go mod init com.zetcode/Simple
We create a new Go module.
$ go get github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2
We include the excelize library to the project.
package main
import (
"log"
"time"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
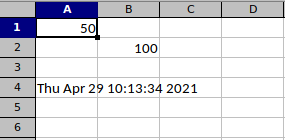
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2", 100)
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1", 50)
now := time.Now()
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A4", now.Format(time.ANSIC))
if err := f.SaveAs("simple.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
We create a new file and write to three cells.
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
We include the excelize package.
f := excelize.NewFile()
A new file is created with NewFile.
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2", 100)
We set an integer value to B2 cell with SetCellValue.
now := time.Now()
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A4", now.Format(time.ANSIC))
Here we write current datetime to cell A4.
if err := f.SaveAs("simple.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
We write the data with SaveAs.
$ go run simple.go
We run the example and then open the simple.xlsx file.
Go read Excel file
In the next example, we read from the previously created Excel file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("simple.xlsx")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
c1, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(c1)
c2, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "A4")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(c2)
c3, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(c3)
}
The example reads from three cells.
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("simple.xlsx")
The simple.xlsx file is opened with OpenFile.
c1, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1")
A cell is read with GetCellValue; we provide the sheet name and the
cell coordinates as parameters.
$ go run read_cell.go 50 Thu Apr 29 10:29:06 2021 100
Go Excel new sheet
A new Excel sheet is created with NewSheet.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1", 50)
idx := f.NewSheet("Sheet2")
fmt.Println(idx)
f.SetCellValue("Sheet2", "A1", 50)
f.SetActiveSheet(idx)
if err := f.SaveAs("new_sheet.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
The example creates a new sheet and writes to a cell.
idx := f.NewSheet("Sheet2")
A new sheet called Sheet2 is created with NewSheet;
the function returns the index to the generated sheet.
f.SetCellValue("Sheet2", "A1", 50)
We write to the Sheet2's A1 cell.
f.SetActiveSheet(idx)
The active sheet is set with SetActiveSheet; it takes the index
of the sheet as parameter.
Go Excel apply style
A style is created with NewStyle and is applied with
SetCellStyle.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
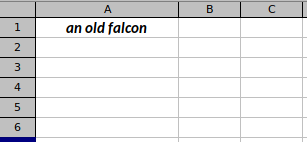
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1", "an old falcon")
f.SetColWidth("Sheet1", "A", "A", 20)
style, _ := f.NewStyle(`{"alignment":{"horizontal":"center"},
"font":{"bold":true,"italic":true}}`)
f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "A1", "A1", style)
if err := f.SaveAs("styled.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
In the code example, we have text in the A1 cell. We center the text horizontally and make the font bold and italic.
Go Excel merge cells
To merge cells, we use the MergeCell function.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
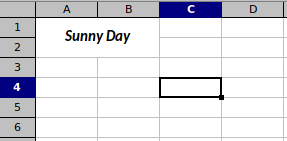
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "A1", "Sunny Day")
f.MergeCell("Sheet1", "A1", "B2")
style, _ := f.NewStyle(`{"alignment":{"horizontal":"center","vertical":"center"},
"font":{"bold":true,"italic":true}}`)
f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "A1", "B2", style)
if err := f.SaveAs("merging.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
We merge four cells into one with MergeCell.
f.MergeCell("Sheet1", "A1", "B2")
The MergeCell function takes the sheet name, and the top-left and
bottom-right cells as parameters.
style, _ := f.NewStyle(`{"alignment":{"horizontal":"center","vertical":"center"},
"font":{"bold":true,"italic":true}}`)
f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "A1", "B2", style)
In addition, we apply style on the merged cells.
Go Excel chart
A new chart is created with AddChart function. It is possible to
create various charts, including column, pie, area, or line charts.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
categories := map[string]string{"A1": "USA", "A2": "China", "A3": "UK",
"A4": "Russia", "A5": "South Korea", "A6": "Germany"}
values := map[string]int{"B1": 46, "B2": 38, "B3": 29, "B4": 22, "B5": 13, "B6": 11}
f := excelize.NewFile()
for k, v := range categories {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
for k, v := range values {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
if err := f.AddChart("Sheet1", "E1", `{
"type":"col",
"series":[
{"name":"Sheet1!$A$2","categories":"Sheet1!$A$1:$A$6",
"values":"Sheet1!$B$1:$B$6"}
],
"title":{"name":"Olympic Gold medals in London 2012"}}`); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := f.SaveAs("gold_medals.xlsx"); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
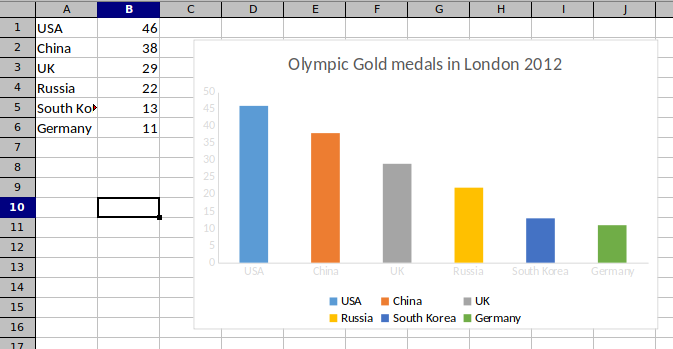
In the code example, we create a column chart to show the number of Olympic gold medals per country in London 2012.
categories := map[string]string{"A1": "USA", "A2": "China", "A3": "UK",
"A4": "Russia", "A5": "South Korea", "A6": "Germany"}
values := map[string]int{"B1": 46, "B2": 38, "B3": 29, "B4": 22, "B5": 13, "B6": 11}
Categories and values are stored in Go maps.
for k, v := range categories {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
for k, v := range values {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
Using two for loops, we insert the data into a sheet.
if err := f.AddChart("Sheet1", "E1", `{
"type":"col",
"series":[
{"name":"Sheet1!$A$2","categories":"Sheet1!$A$1:$A$6",
"values":"Sheet1!$B$1:$B$6"}
],
"title":{"name":"Olympic Gold medals in London 2012"}}`); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
A chart is created with AddChart. We provide the type of the chart
and the series data.
Source
In this article we have demonstrated how to read and write to Excel files with Go using excelize library.
Author
List all Go tutorials.