Shapes and fills in PyCairo
last modified July 17, 2023
In this part of the PyCairo tutorial, we create some basic and more advanced shapes. We fill these shapes with solid colors, patterns, and gradients. Gradients will be covered in a separate chapter.
Basic shapes
PyCairo has some basic methods to create simple shapes.
def on_draw(self, wid, cr):
cr.set_source_rgb(0.6, 0.6, 0.6)
cr.rectangle(20, 20, 120, 80)
cr.rectangle(180, 20, 80, 80)
cr.fill()
cr.arc(330, 60, 40, 0, 2*math.pi)
cr.fill()
cr.arc(90, 160, 40, math.pi/4, math.pi)
cr.fill()
cr.translate(220, 180)
cr.scale(1, 0.7)
cr.arc(0, 0, 50, 0, 2*math.pi)
cr.fill()
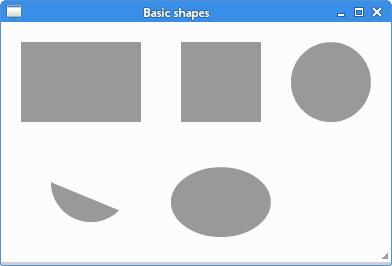
In this example, we create a rectangle, a square, a circle, an arc, and an ellipse.
cr.rectangle(20, 20, 120, 80) cr.rectangle(180, 20, 80, 80)
The rectangle method is used to create both
squares and rectangles. A square is just a specific type of
a rectangle. The parameters are the x and y coordinates of
the top-left corner of the window and the width and height
of the rectangle.
cr.arc(330, 60, 40, 0, 2*math.pi)
The arc method creates a circle. The parameters
are the x and y coordinates of the center of the arc, the
radius, and the start and end angles, in radians.
cr.arc(90, 160, 40, math.pi/4, math.pi)
Here we draw an arc, a portion of a circle.
cr.scale(1, 0.7) cr.arc(0, 0, 50, 0, 2*math.pi)
We use the scale and the arc methods to create
an ellipse.
Other shapes can be created using a combination of basic primitives.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This code example draws another
three shapes in PyCairo.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
from gi.repository import Gtk
import cairo
class cv(object):
points = (
( 0, 85 ),
( 75, 75 ),
( 100, 10 ),
( 125, 75 ),
( 200, 85 ),
( 150, 125 ),
( 160, 190 ),
( 100, 150 ),
( 40, 190 ),
( 50, 125 ),
( 0, 85 )
)
class Example(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.init_ui()
def init_ui(self):
darea = Gtk.DrawingArea()
darea.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
self.add(darea)
self.set_title("Complex shapes")
self.resize(460, 240)
self.set_position(Gtk.WindowPosition.CENTER)
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def on_draw(self, wid, cr):
cr.set_source_rgb(0.6, 0.6, 0.6)
cr.set_line_width(1)
for i in range(10):
cr.line_to(cv.points[i][0], cv.points[i][1])
cr.fill()
cr.move_to(240, 40)
cr.line_to(240, 160)
cr.line_to(350, 160)
cr.fill()
cr.move_to(380, 40)
cr.line_to(380, 160)
cr.line_to(450, 160)
cr.curve_to(440, 155, 380, 145, 380, 40)
cr.fill()
def main():
app = Example()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
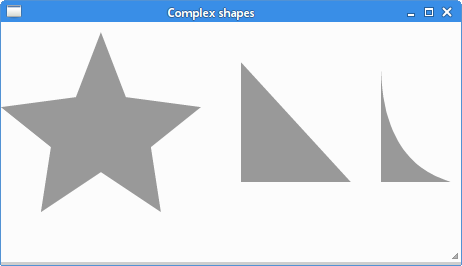
In this example, we create a star object, a triangle, and a modified triangle. These objects are created using lines and one curve.
for i in range(10):
cr.line_to(cv.points[i][0], cv.points[i][1])
cr.fill()
The star is drawn by joining all the points that are in the points tuple.
The fill method fills the star object with the current color.
cr.move_to(240, 40) cr.line_to(240, 160) cr.line_to(350, 160) cr.fill()
These lines create a triangle. The last two points are automatically joined.
cr.move_to(380, 40) cr.line_to(380, 160) cr.line_to(450, 160) cr.curve_to(440, 155, 380, 145, 380, 40) cr.fill()
The modified triangle is a simple combination of two lines and one curve.
Fills
Fills fill the interiors of shapes. Fills can be solid colors, patters, or gradients.
Solid colors
A color is an object representing a combination of Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) intensity values. PyCairo valid RGB values are in the range 0 to 1.
def on_draw(self, wid, cr):
cr.set_source_rgb(0.2, 0.23, 0.9)
cr.rectangle(10, 15, 90, 60)
cr.fill()
cr.set_source_rgb(0.9, 0.1, 0.1)
cr.rectangle(130, 15, 90, 60)
cr.fill()
cr.set_source_rgb(0.4, 0.9, 0.4)
cr.rectangle(250, 15, 90, 60)
cr.fill()
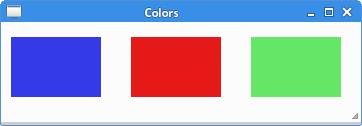
In the example we draw four colored rectangles.
cr.set_source_rgb(0.2, 0.23, 0.9) cr.rectangle(10, 15, 90, 60) cr.fill()
The set_source_rgb method sets the source to an opaque color.
The parameters are the Red, Green, Blue intensity values.
The source is used to fill the interior of a rectangle by calling the
fill method.
Patterns
Patterns are complex graphical objects that can be used to fill shapes.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This program shows how to work
with patterns in PyCairo.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
from gi.repository import Gtk
import cairo
class Example(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.init_ui()
self.create_surpat()
def init_ui(self):
darea = Gtk.DrawingArea()
darea.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
self.add(darea)
self.set_title("Patterns")
self.resize(300, 290)
self.set_position(Gtk.WindowPosition.CENTER)
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def create_surpat(self):
sr1 = cairo.ImageSurface.create_from_png("blueweb.png")
sr2 = cairo.ImageSurface.create_from_png("maple.png")
sr3 = cairo.ImageSurface.create_from_png("crack.png")
sr4 = cairo.ImageSurface.create_from_png("chocolate.png")
self.pt1 = cairo.SurfacePattern(sr1)
self.pt1.set_extend(cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT)
self.pt2 = cairo.SurfacePattern(sr2)
self.pt2.set_extend(cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT)
self.pt3 = cairo.SurfacePattern(sr3)
self.pt3.set_extend(cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT)
self.pt4 = cairo.SurfacePattern(sr4)
self.pt4.set_extend(cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT)
def on_draw(self, wid, cr):
cr.set_source(self.pt1)
cr.rectangle(20, 20, 100, 100)
cr.fill()
cr.set_source(self.pt2)
cr.rectangle(150, 20, 100, 100)
cr.fill()
cr.set_source(self.pt3)
cr.rectangle(20, 140, 100, 100)
cr.fill()
cr.set_source(self.pt4)
cr.rectangle(150, 140, 100, 100)
cr.fill()
def main():
app = Example()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
In this example, we draw four rectangles. This time we fill them with some patterns. We use four pattern images from the Gimp image manipulation program. We must retain the original size of those patterns because we are going to tile them.
We create image surfaces outside the draw method.
It would not be efficient to read from harddisk each time the window needs to be redrawn.
sr1 = cairo.ImageSurface.create_from_png("blueweb.png")
An image surface is created from a PNG image.
self.pt1 = cairo.SurfacePattern(sr1) self.pt1.set_extend(cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT)
A pattern is created from the surface. We set the mode to
cairo.EXTEND_REPEAT which causes the
pattern to be tiled by repeating.
cr.set_source(self.pt1) cr.rectangle(20, 20, 100, 100) cr.fill()
Here we draw our first rectangle. The set_source method tells
the Cairo context to use a pattern as a source for drawing. The image patterns may not
fit exactly the shape. The rectangle creates a rectangular path.
Finally, the fill method fills the path with the source.
This chapter covered PyCairo shapes and fills.