PyCairo backends
last modified July 17, 2023
PyCairo supports various backends. Backends are places where the graphics produced by PyCairo can be displayed. We use PyCairo to create a PNG image, a PDF file, a SVG file, and we draw on a GTK window.
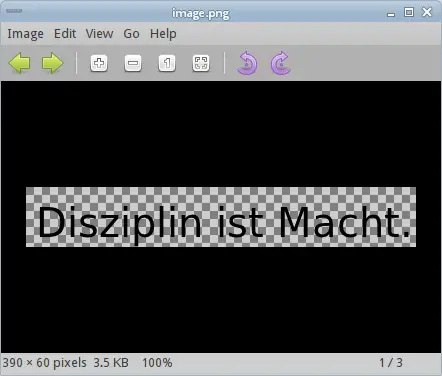
PNG image
In the first example we create a PNG image.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This program uses PyCairo to
produce a PNG image.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
import cairo
def main():
ims = cairo.ImageSurface(cairo.FORMAT_ARGB32, 390, 60)
cr = cairo.Context(ims)
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.select_font_face("Sans", cairo.FONT_SLANT_NORMAL,
cairo.FONT_WEIGHT_NORMAL)
cr.set_font_size(40)
cr.move_to(10, 50)
cr.show_text("Disziplin ist Macht.")
ims.write_to_png("image.png")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
This example is a small console application that creates a PNG image.
import cairo
We import the PyCairo module.
ims = cairo.ImageSurface(cairo.FORMAT_ARGB32, 390, 60) cr = cairo.Context(ims)
We create a surface and a Cairo context from the surface. The surface is a 390x60 px image.
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
We draw our text in black ink. The ink is specified with the
set_source_rgb method.
cr.select_font_face("Sans", cairo.FONT_SLANT_NORMAL,
cairo.FONT_WEIGHT_NORMAL)
cr.set_font_size(40)
We choose a font type with the select_font_face method
and set its size with the set_font_size method.
cr.move_to(10, 50)
cr.show_text("Disziplin ist Macht.")
We move to a position at x=10.0, y=50.0 within the image and draw the text.
ims.write_to_png("image.png")
The write_to_png method writes the contents of the
surface to the PNG image.
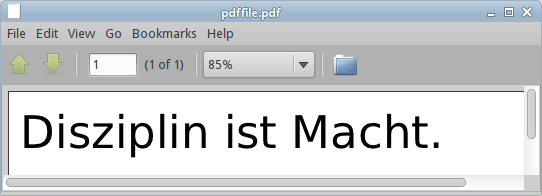
PDF file
In the second example, we create a simple PDF file.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This program uses PyCairo to
produce a PDF image.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
import cairo
def main():
ps = cairo.PDFSurface("pdffile.pdf", 504, 648)
cr = cairo.Context(ps)
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.select_font_face("Sans", cairo.FONT_SLANT_NORMAL,
cairo.FONT_WEIGHT_NORMAL)
cr.set_font_size(40)
cr.move_to(10, 50)
cr.show_text("Disziplin ist Macht.")
cr.show_page()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
We must open the PDF file in a PDF viewer. Linux users can use KPDF or Evince viewers.
ps = cairo.PDFSurface("pdffile.pdf", 504, 648)
To render a PDF file, we must create a PDF surface using the
cairo.PDFSurface object.
The size of the PDF file is specified in points, which is a standard
in typesetting.
cr.show_page()
The show_page finishes rendering of the PDF file.
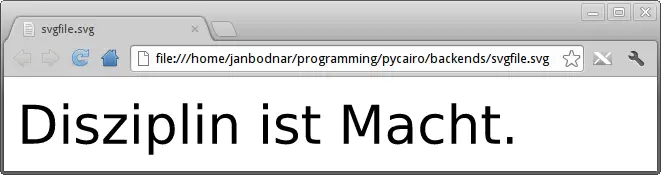
SVG file
The next example creates a simple SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) file. A SVG file is a XML based file format.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This program uses PyCairo to
produce a SVG file.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
import cairo
def main():
ps = cairo.SVGSurface("svgfile.svg", 390, 60)
cr = cairo.Context(ps)
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.select_font_face("Sans", cairo.FONT_SLANT_NORMAL,
cairo.FONT_WEIGHT_NORMAL)
cr.set_font_size(40)
cr.move_to(10, 50)
cr.show_text("Disziplin ist Macht.")
cr.show_page()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
We can use a web browser like Google Chrome or a vector drawing program like Inkscape to open a SVG file.
ps = cairo.SVGSurface("svgfile.svg", 390, 60)
To create a SVG file in PyCairo, we must create a SVG surface using the
cairo.SVGSurface object.
cr.show_page()
The show_page method call finisheds rendering of
the SVG file.
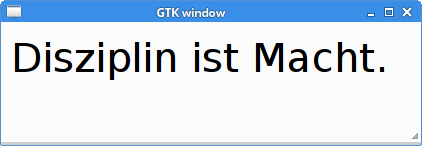
GTK Window
In the last example, we draw on a GTK window. This backend will be used throughout the rest of the tutorial.
#!/usr/bin/python
'''
ZetCode PyCairo tutorial
This program uses PyCairo to
draw on a window in GTK.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
'''
from gi.repository import Gtk
import cairo
class Example(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.init_ui()
def init_ui(self):
darea = Gtk.DrawingArea()
darea.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
self.add(darea)
self.set_title("GTK window")
self.resize(420, 120)
self.set_position(Gtk.WindowPosition.CENTER)
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def on_draw(self, wid, cr):
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.select_font_face("Sans", cairo.FONT_SLANT_NORMAL,
cairo.FONT_WEIGHT_NORMAL)
cr.set_font_size(40)
cr.move_to(10, 50)
cr.show_text("Disziplin ist Macht.")
def main():
app = Example()
Gtk.main()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The example pops up a centered GTK window on which we draw the "Disziplin ist Macht" text.
from gi.repository import Gtk import cairo
We import the necessary PyCairo and GTK modules.
darea = Gtk.DrawingArea()
We draw on a Gtk.DrawingArea widget.
darea.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
When the window is redrawn, a draw signal is emitted. We connect
that signal to the on_draw callback.
def on_draw(self, wid, cr): ...
The drawing is done inside the on_draw method. The third parameter
is the cairo context. It is automatically available to us; the Cairo library is
built into the GTK system.
In this chapter we have covered supported PyCairo backends.