wxPython Gripts
last modified January 10, 2023
In this section we will show some small, complete scripts. These graphical scripts or "gripts" will demonstrate various areas in programming.
We present three gripts. The first will send an email message. The second will connect to the anonymous FTP account and display a connected or disconnected image in the statusbar. The final one will create a small puzzle game.
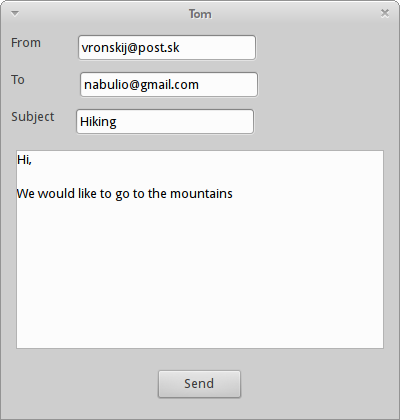
Tom
Tom is a simple script that sends an email.
#!/usr/bin/python
import wx
import smtplib
class Example(wx.Dialog):
def __init__(self, *args, **kw):
super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)
self.InitUI()
def InitUI(self):
pnl = wx.Panel(self)
vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
hbox1 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
hbox2 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
hbox3 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='From')
st2 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='To ')
st3 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Subject')
self.tc1 = wx.TextCtrl(pnl, size=(180, -1))
self.tc2 = wx.TextCtrl(pnl, size=(180, -1))
self.tc3 = wx.TextCtrl(pnl, size=(180, -1))
self.tc = wx.TextCtrl(pnl, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE)
button_send = wx.Button(pnl, label='Send')
hbox1.Add(st1, flag=wx.LEFT, border=10)
hbox1.Add(self.tc1, flag=wx.LEFT, border=35)
hbox2.Add(st2, flag=wx.LEFT, border=10)
hbox2.Add(self.tc2, flag=wx.LEFT, border=50)
hbox3.Add(st3, flag=wx.LEFT, border=10)
hbox3.Add(self.tc3, flag=wx.LEFT, border=20)
vbox.Add(hbox1, flag=wx.TOP, border=10)
vbox.Add(hbox2, flag=wx.TOP, border=10)
vbox.Add(hbox3, flag=wx.TOP, border=10)
vbox.Add(self.tc, proportion=1, flag=wx.EXPAND | wx.TOP |
wx.RIGHT | wx.LEFT, border=15)
vbox.Add(button_send, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTER | wx.TOP |
wx.BOTTOM, border=20)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnSend, button_send)
pnl.SetSizer(vbox)
self.SetSize((400, 420))
self.SetTitle('Tom')
self.Centre()
self.ShowModal()
self.Destroy()
def OnSend(self, e):
sender = self.tc1.GetValue()
recipient = self.tc2.GetValue()
subject = self.tc3.GetValue()
text = self.tc.GetValue()
header = 'From: %s\r\nTo: %s\r\nSubject: %s\r\n\r\n' %
(sender, recipient, subject)
message = header + text
try:
server = smtplib.SMTP('mail.chello.sk')
server.sendmail(sender, recipient, message)
server.quit()
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, 'Email was successfully sent', 'Success',
wx.OK | wx.ICON_INFORMATION)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
except smtplib.SMTPException, error:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(self, 'Failed to send email',
'Error', wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)
dlg.ShowModal()
dlg.Destroy()
def main():
ex = wx.App()
Example(None)
ex.MainLoop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
We have a dialog window with from, to and subject text controls and a message text control. After pushing the send button the email is sent to the recipient.
import smtplib
For working with emails we need to import SMTP module. This module is part of the Python language.
header = 'From: %s\r\nTo: %s\r\nSubject: %s\r\n\r\n' %
(sender, recipient, subject)
From, To and Subject options must be separated by carriage return and newline as shown here. This is requested by RFC 821 norm. So we must follow it.
server = smtplib.SMTP('mail.chello.sk')
server.sendmail(sender, recipient, message)
server.quit()
Next we create an SMTP connection. Here you specify your settings. Each ISP gives you
the name of the pop and SMTP servers. In our case, 'mail.chello.sk' is a name for both.
A mail is sent by calling the sendmail() method. Finally, we quit the
connection with the quit() method.
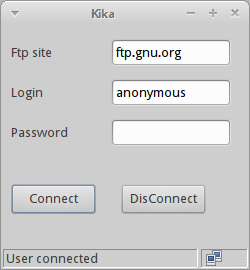
Kika
Kika is a gript that connects to an FTP site. If a login is successful,
Kika shows a connected icon on the statusbar. Otherwise, a disconnected
icon is displayed. We use an ftplib module from the Python
standard library. If you do not have an FTP account, you can try to login
to some anonymous FTP sites.
#!/usr/bin/python
from ftplib import FTP, all_errors
import wx
class MyStatusBar(wx.StatusBar):
def __init__(self, parent):
super(MyStatusBar, self).__init__(parent)
self.SetFieldsCount(2)
self.SetStatusText('Welcome to Kika', 0)
self.SetStatusWidths([-1, 50])
self.icon = wx.StaticBitmap(self, bitmap=wx.Bitmap('disconnected.png'))
self.Bind(wx.EVT_SIZE, self.OnSize)
self.PlaceIcon()
def PlaceIcon(self):
rect = self.GetFieldRect(1)
self.icon.SetPosition((rect.x+5, rect.y+1))
def OnSize(self, e):
e.Skip()
self.PlaceIcon()
class Example(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, *args, **kw):
super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)
self.InitUI()
def InitUI(self):
wx.StaticText(self, label='Ftp site', pos=(10, 20))
wx.StaticText(self, label='Login', pos=(10, 60))
wx.StaticText(self, label='Password', pos=(10, 100))
self.ftpsite = wx.TextCtrl(self, pos=(110, 15),
size=(120, -1))
self.login = wx.TextCtrl(self, pos=(110, 55),
size=(120, -1))
self.password = wx.TextCtrl(self, pos=(110, 95),
size=(120, -1), style=wx.TE_PASSWORD)
self.ftp = None
con = wx.Button(self, label='Connect', pos=(10, 160))
discon = wx.Button(self, label='DisConnect', pos=(120, 160))
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnConnect, con)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnDisConnect, discon)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_MAXIMIZE, self.OnMaximize)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_SHOW, self.OnShown)
self.sb = MyStatusBar(self)
self.SetStatusBar(self.sb)
self.SetSize((250, 270))
self.SetTitle('Kika')
self.Centre()
self.Show()
def OnShown(self, e):
if self.sb:
self.sb.PlaceIcon()
def OnMaximize(self, e):
self.sb.PlaceIcon()
def OnConnect(self, e):
if not self.ftp:
ftpsite = self.ftpsite.GetValue()
login = self.login.GetValue()
password = self.password.GetValue()
try:
self.ftp = FTP(ftpsite)
var = self.ftp.login(login, password)
self.sb.SetStatusText('User connected')
self.sb.icon.SetBitmap(wx.Bitmap('connected.png'))
except AttributeError:
self.sb.SetStatusText('Incorrect params')
self.ftp = None
except all_errors, err:
self.sb.SetStatusText(str(err))
self.ftp = None
def OnDisConnect(self, e):
if self.ftp:
self.ftp.quit()
self.ftp = None
self.sb.SetStatusText('User disconnected')
self.sb.icon.SetBitmap(wx.Bitmap('disconnected.png'))
def main():
ex = wx.App()
Example(None)
ex.MainLoop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In the code example, we will connect to an FTP site and show connected or disconnected icons in the statusbar.
from ftplib import FTP, all_errors
We use the standard ftplib Python module.
self.SetFieldsCount(2)
self.SetStatusText('Welcome to Kika', 0)
self.SetStatusWidths([-1, 50])
Our custom statusbar will have two fields. A welcome message is shown
in the first field of the statusbar with the SetStatusText()
method. The SetStatusWidths() method arranges the width for the
status fields. The second field has a fixed width, the first one takes the
rest of the statusbar's width.
def PlaceIcon(self):
rect = self.GetFieldRect(1)
self.icon.SetPosition((rect.x+5, rect.y+1))
The PlaceIcon() method positions the icon on the statusbar.
With the GetFieldRect() method we determine the size of the
second field of the statusbar. Later we place the icon using the
SetPosition() method.
def OnSize(self, e):
e.Skip()
self.PlaceIcon()
Notice that each time the window is resized, we must position our icon to a new place.
self.Bind(wx.EVT_MAXIMIZE, self.OnMaximize) self.Bind(wx.EVT_SHOW, self.OnShown)
We also react to wx.EVT_MAXIMIZE and wx.EVT_SHOW
events. In their event handlers, we replace the icon on the statusbar.
try:
self.ftp = FTP(ftpsite)
var = self.ftp.login(login, password)
self.sb.SetStatusText('User connected')
self.sb.icon.SetBitmap(wx.Bitmap('connected.png'))
We login to the provided ftp site. A connected icon is shown in the statusbar.
def OnDisConnect(self, e):
if self.ftp:
self.ftp.quit()
self.ftp = None
self.sb.SetStatusText('User disconnected')
self.sb.icon.SetBitmap(wx.Bitmap('disconnected.png'))
In the OnDisConnect() method, we quit the connection to the
ftp site if there is any. The statusbar will show a
disconnected icon.
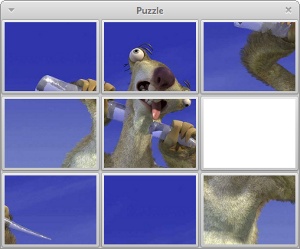
Puzzle
In this gript, we introduce a puzzle game. We have an image of a Sid character from the Ice Age movie. The goal is to form the picture.
$ convert sid.png -crop 120x90 sid%d.png $ ls sid0.png sid2.png sid4.png sid6.png sid8.png sid1.png sid3.png sid5.png sid7.png sid.png
ImageMagick program can be used to easily slice an image to smaller images. If your image is 360x270, the above command will crop the image into nine parts.
#!/usr/bin/python
import wx
import random
class Example(wx.Dialog):
def __init__(self, *args, **kw):
super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw)
self.InitUI()
def InitUI(self):
images = ['sid1.png', 'sid2.png', 'sid3.png', 'sid4.png',
'sid5.png', 'sid6.png', 'sid7.png', 'sid8.png']
self.pos = [ [0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8] ]
self.sizer = wx.GridSizer(3, 3, 0, 0)
numbers = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
random.shuffle(numbers)
for i in numbers:
btn = wx.BitmapButton(self, i, wx.Bitmap(images[i]))
btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnPressButton, btn)
self.sizer.Add(btn)
self.empty = wx.BitmapButton(self, bitmap=wx.Bitmap('empty.png'))
self.empty.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnPressButton, self.empty)
self.sizer.Add(self.empty)
self.SetSizerAndFit(self.sizer)
self.SetTitle('Puzzle')
self.Centre()
self.ShowModal()
self.Destroy()
def OnPressButton(self, e):
btn = e.GetEventObject()
width = self.empty.GetSize().x
height = self.empty.GetSize().y
btnX = btn.GetPosition().x
btnY = btn.GetPosition().y
emptyX = self.empty.GetPosition().x
emptyY = self.empty.GetPosition().y
if (((btnX == emptyX) and (emptyY - btnY) == height)
or ((btnX == emptyX) and (emptyY - btnY) == -height)
or ((btnY == emptyY) and (emptyX - btnX) == width)
or ((btnY == emptyY) and (emptyX - btnX) == -width)):
self.ExchangeImages(btn)
def ExchangeImages(self, btn):
bmp1 = self.empty.GetBitmapLabel()
bmp2 = btn.GetBitmapLabel()
self.empty.SetBitmapLabel(bmp2)
btn.SetBitmapLabel(bmp1)
self.empty = btn
def main():
ex = wx.App()
Example(None)
ex.MainLoop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The image is sliced into 9 subimages. 8 subimages are used in the program. One empty image is used as well.
images = ['sid1.png', 'sid2.png', 'sid3.png', 'sid4.png',
'sid5.png', 'sid6.png', 'sid7.png', 'sid8.png']
These are the images that will be shown in button widgets.
self.sizer = wx.GridSizer(3, 3, 0, 0)
For this gript, wx.GridSizer fits ideally.
numbers = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] random.shuffle(numbers)
We have eight numbers. Those numbers are shuffled so that we have a random number order. Each time we start the gript, we will have a different order of bitmaps.
for i in numbers:
btn = wx.BitmapButton(self, i, wx.Bitmap(images[i]))
btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnPressButton, btn)
self.sizer.Add(btn)
In this for loop, we create 8 bitmap buttons with the provided images. To each button an event handler is attached.
self.empty = wx.BitmapButton(self, bitmap=wx.Bitmap('empty.png'))
self.empty.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnPressButton, self.empty)
self.sizer.Add(self.empty)
The ninth button displays an empty image. The self.empty variable serves as a pointer to the button, which has an empty image. Buttons will exchange their images so the self.empty variable will point to different buttons over time.
def OnPressButton(self, e):
btn = e.GetEventObject()
width = self.empty.GetSize().x
height = self.empty.GetSize().y
...
When we press a button, the OnPressButton() handler is called.
The GetEventObject() method retrieves the event source;
it is the button that triggerd the wx.EVT_BUTTON event.
We get the width and height of the emtpy button. (All the buttons
have the same size). These values will be used to determine the
buttons adjacent to the empty button.
btnX = btn.GetPosition().x btnY = btn.GetPosition().y emptyX = self.empty.GetPosition().x emptyY = self.empty.GetPosition().y
We get the x, y coordinates of the currently pressed button and the empty button.
if (((btnX == emptyX) and (emptyY - btnY) == height)
or ((btnX == emptyX) and (emptyY - btnY) == -height)
or ((btnY == emptyY) and (emptyX - btnX) == width)
or ((btnY == emptyY) and (emptyX - btnX) == -width)):
self.ExchangeImages(btn)
Here we find out if the pressed button is adjacent to the
empty button. If true, we call the ExchangeImages() method
which will switch the images for the two buttons.
def ExchangeImages(self, btn):
bmp1 = self.empty.GetBitmapLabel()
bmp2 = btn.GetBitmapLabel()
self.empty.SetBitmapLabel(bmp2)
btn.SetBitmapLabel(bmp1)
self.empty = btn
In the ExchangeImages() method, we get the images of the
two buttons in question. We switch them. Finally, the
self.empty button points to the new button, which has the
empty image.
In this chapter, we have presented three interesting gripts.