Kotlin Snake
last modified January 29, 2024
This article shows how to create a snake game in Kotlin with Swing.
The source code and the images are available at the author's Github Kotlin-Snake-Game repository.
Snake
Snake is an older classic video game. It was first created in late 70s. Later it was brought to PCs. In this game the player controls a snake. The objective of the game is to eat as many apples as possible. When the snake eats an apple its body grows. The snake has to avoid the walls and its own body. This game is sometimes called Nibbles.
Swing
Swing is the principal GUI toolkit for the Java programming language. It is a part of the JFC (Java Foundation Classes), which is an API for providing a graphical user interface for Java programs.
Kotlin Sname game
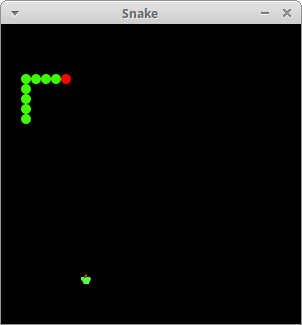
The size of each of the joints of a snake is 10 px. The snake is controlled with the cursor keys. Initially, the snake has three joints. If the game is finished, the "Game Over" message is displayed in the middle of the board.
package com.zetcode
import java.awt.*
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent
import java.awt.event.ActionListener
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent
import javax.swing.ImageIcon
import javax.swing.JPanel
import javax.swing.Timer
class Board : JPanel(), ActionListener {
private val boardWidth = 300
private val boardHeight = 300
private val dotSize = 10
private val allDots = 900
private val randPos = 29
private val delay = 140
private val x = IntArray(allDots)
private val y = IntArray(allDots)
private var nOfDots: Int = 0
private var appleX: Int = 0
private var appleY: Int = 0
private var leftDirection = false
private var rightDirection = true
private var upDirection = false
private var downDirection = false
private var inGame = true
private var timer: Timer? = null
private var ball: Image? = null
private var apple: Image? = null
private var head: Image? = null
init {
addKeyListener(TAdapter())
background = Color.black
isFocusable = true
preferredSize = Dimension(boardWidth, boardHeight)
loadImages()
initGame()
}
private fun loadImages() {
val iid = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/dot.png")
ball = iid.image
val iia = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/apple.png")
apple = iia.image
val iih = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/head.png")
head = iih.image
}
private fun initGame() {
nOfDots = 3
for (z in 0 until nOfDots) {
x[z] = 50 - z * 10
y[z] = 50
}
locateApple()
timer = Timer(delay, this)
timer!!.start()
}
public override fun paintComponent(g: Graphics) {
super.paintComponent(g)
doDrawing(g)
}
private fun doDrawing(g: Graphics) {
if (inGame) {
g.drawImage(apple, appleX, appleY, this)
for (z in 0 until nOfDots) {
if (z == 0) {
g.drawImage(head, x[z], y[z], this)
} else {
g.drawImage(ball, x[z], y[z], this)
}
}
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().sync()
} else {
gameOver(g)
}
}
private fun gameOver(g: Graphics) {
val msg = "Game Over"
val small = Font("Helvetica", Font.BOLD, 14)
val fontMetrics = getFontMetrics(small)
val rh = RenderingHints(
RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON)
rh[RenderingHints.KEY_RENDERING] = RenderingHints.VALUE_RENDER_QUALITY
(g as Graphics2D).setRenderingHints(rh)
g.color = Color.white
g.font = small
g.drawString(msg, (boardWidth - fontMetrics.stringWidth(msg)) / 2,
boardHeight / 2)
}
private fun checkApple() {
if (x[0] == appleX && y[0] == appleY) {
nOfDots++
locateApple()
}
}
private fun move() {
for (z in nOfDots downTo 1) {
x[z] = x[z - 1]
y[z] = y[z - 1]
}
if (leftDirection) {
x[0] -= dotSize
}
if (rightDirection) {
x[0] += dotSize
}
if (upDirection) {
y[0] -= dotSize
}
if (downDirection) {
y[0] += dotSize
}
}
private fun checkCollision() {
for (z in nOfDots downTo 1) {
if (z > 4 && x[0] == x[z] && y[0] == y[z]) {
inGame = false
}
}
if (y[0] >= boardHeight) {
inGame = false
}
if (y[0] < 0) {
inGame = false
}
if (x[0] >= boardWidth) {
inGame = false
}
if (x[0] < 0) {
inGame = false
}
if (!inGame) {
timer!!.stop()
}
}
private fun locateApple() {
var r = (Math.random() * randPos).toInt()
appleX = r * dotSize
r = (Math.random() * randPos).toInt()
appleY = r * dotSize
}
override fun actionPerformed(e: ActionEvent) {
if (inGame) {
checkApple()
checkCollision()
move()
}
repaint()
}
private inner class TAdapter : KeyAdapter() {
override fun keyPressed(e: KeyEvent?) {
val key = e!!.keyCode
if (key == KeyEvent.VK_LEFT && !rightDirection) {
leftDirection = true
upDirection = false
downDirection = false
}
if (key == KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT && !leftDirection) {
rightDirection = true
upDirection = false
downDirection = false
}
if (key == KeyEvent.VK_UP && !downDirection) {
upDirection = true
rightDirection = false
leftDirection = false
}
if (key == KeyEvent.VK_DOWN && !upDirection) {
downDirection = true
rightDirection = false
leftDirection = false
}
}
}
}
First we will define the properties used in our game.
private val boardWidth = 300 private val boardHeight = 300 private val dotSize = 10 private val allDots = 900 private val randPos = 29 private val delay = 140
The boardWidth and boardHeight properties determine the size
of the board. The dotSize is the size of the apple and the dot of
the snake. The allDots property defines the maximum number
of possible dots on the board (900 = (300*300)/(10*10)). The randPos
property is used to calculate a random position for an apple. The
delay property determines the speed of the game.
private val x = IntArray(allDots) private val y = IntArray(allDots)
These two arrays store the x and y coordinates of all joints of a snake.
private fun loadImages() {
val iid = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/dot.png")
ball = iid.image
val iia = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/apple.png")
apple = iia.image
val iih = ImageIcon("src/main/resources/head.png")
head = iih.image
}
In the loadImages method we get the images for the game.
The ImageIcon class is used for displaying PNG images.
private fun initGame() {
nOfDots = 3
for (z in 0 until nOfDots) {
x[z] = 50 - z * 10
y[z] = 50
}
locateApple()
timer = Timer(delay, this)
timer!!.start()
}
In the initGame method we create the snake, randomly locate
an apple on the board, and start the timer.
private fun doDrawing(g: Graphics) {
if (inGame) {
g.drawImage(apple, appleX, appleY, this)
for (z in 0 until nOfDots) {
if (z == 0) {
g.drawImage(head, x[z], y[z], this)
} else {
g.drawImage(ball, x[z], y[z], this)
}
}
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().sync()
} else {
gameOver(g)
}
}
In the doDrawing method, we draw the apple and the snake
objects. If the game has finished, we draw game over message.
private fun gameOver(g: Graphics) {
val msg = "Game Over"
val small = Font("Helvetica", Font.BOLD, 14)
val fontMetrics = getFontMetrics(small)
val rh = RenderingHints(
RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON)
rh[RenderingHints.KEY_RENDERING] = RenderingHints.VALUE_RENDER_QUALITY
(g as Graphics2D).setRenderingHints(rh)
g.color = Color.white
g.font = small
g.drawString(msg, (boardWidth - fontMetrics.stringWidth(msg)) / 2,
boardHeight / 2)
}
The gameOver method draws "Game Over" message in the
middle of the window. We use rendering hints to draw the message smoothly.
We use font metrics to get the size of the message.
private fun checkApple() {
if (x[0] == appleX && y[0] == appleY) {
nOfDots++
locateApple()
}
}
If the apple collides with the head, we increase the number of joints of the snake.
We call the locateApple method which randomly positions a new apple object.
In the move method we have the key algorithm of the game. To
understand it, look at how the snake is moving. We control
the head of the snake. We can change its direction with the cursor keys.
The rest of the joints move one position up the chain. The second joint
moves where the first was, the third joint where the second was etc.
for (z in nOfDots downTo 1) {
x[z] = x[z - 1]
y[z] = y[z - 1]
}
This code moves the joints up the chain.
if (leftDirection) {
x[0] -= dotSize
}
This line moves the head to the left.
In the checkCollision method, we determine if
the snake has hit itself or one of the walls.
for (z in nOfDots downTo 1) {
if (z > 4 && x[0] == x[z] && y[0] == y[z]) {
inGame = false
}
}
If the snake hits one of its joints with its head the game is over.
if (y[0] >= boardHeight) {
inGame = false
}
The game is finished if the snake hits the bottom of the board.
package com.zetcode
import java.awt.EventQueue
import javax.swing.JFrame
class Snake : JFrame() {
init {
initUI()
}
private fun initUI() {
add(Board())
title = "Snake"
isResizable = false
pack()
setLocationRelativeTo(null)
defaultCloseOperation = JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun main() {
EventQueue.invokeLater {
val ex = Snake()
ex.isVisible = true
}
}
}
}
This is the main class.
isResizable = false pack()
The isResizable property affects the insets of the JFrame
container on some platforms. Therefore, it is important to call it before the
pack method. Otherwise, the collision of the snake's head with the
right and bottom borders might not work correctly.
Source
This was the Snake game in Kotlin and Swing.
Author
List all Kotlin tutorials.