Drag and Drop in PySide
last modified October 18, 2023
In this part of the PySide tutorial, we talk about drag & drop operations.
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag-and-drop is the action of (or support for the action of) clicking on a virtual object and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, it can be used to invoke many kinds of actions, or create various types of associations between two abstract objects. (Wikipedia)
Drag and drop functionality is one of the most visible aspects of the graphical user interface. Drag and drop operation enables users to do complex things intuitively.
Usually, we can drag and drop two things. Data or some graphical objects. If we drag an image from one application to another, we drag and drop binary data. If we drag a tab in Firefox and move it to another place, we drag and drop a graphical component.
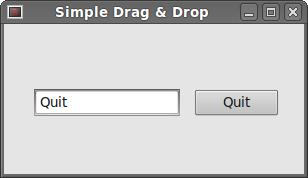
Simple Drag and Drop
In the first example, we have a QtGui.QLineEdit and a
QtGui.QPushButton. We drag plain text from
the line edit widget and drop it onto the button widget.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
This is a simple drag and
drop example.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui, QtCore
class Button(QtGui.QPushButton):
def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent)
self.setAcceptDrops(True)
def dragEnterEvent(self, e):
if e.mimeData().hasFormat('text/plain'):
e.accept()
else:
e.ignore()
def dropEvent(self, e):
self.setText(e.mimeData().text())
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
qe = QtGui.QLineEdit('', self)
qe.setDragEnabled(True)
qe.move(30, 65)
button = Button("Button", self)
button.move(190, 65)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Simple Drag & Drop')
self.show()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Simple drag & drop operation.
class Button(QtGui.QPushButton):
def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent)
In order to drop text on the QtGui.QPushButton widget, we
must reimplement some methods. So we create
our own Button class, which will inherit from the QtGui.QPushButton class.
self.setAcceptDrops(True)
We enable drop events for the widget.
def dragEnterEvent(self, e):
if e.mimeData().hasFormat('text/plain'):
e.accept()
else:
e.ignore()
First we reimplement the dragEnterEvent method.
We inform about the data type, we accept. In our case it is
plain text.
def dropEvent(self, e):
self.setText(e.mimeData().text())
By reimplementing the dropEvent method we define what
we do upon the drop event. Here we change the text of the button widget.
qe = QtGui.QLineEdit('', self)
qe.setDragEnabled(True)
The QtGui.QLineEdit widget has a built-in support for drag operations.
All we need to do is to call setDragEnabled method
to activate it.
Drag & drop a button widget
In the following example, we demonstrate, how to drag & drop a button widget.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PySide tutorial
In this example, we drag and drop a
button.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PySide import QtGui, QtCore
class Button(QtGui.QPushButton):
def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent)
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):
if e.buttons() != QtCore.Qt.RightButton:
return
mimeData = QtCore.QMimeData()
drag = QtGui.QDrag(self)
drag.setMimeData(mimeData)
drag.setHotSpot(e.pos() - self.rect().topLeft())
dropAction = drag.start(QtCore.Qt.MoveAction)
def mousePressEvent(self, e):
QtGui.QPushButton.mousePressEvent(self, e)
if e.button() == QtCore.Qt.LeftButton:
print 'press'
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setAcceptDrops(True)
self.btn = Button('Button', self)
self.btn.move(100, 65)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Click or move')
self.show()
def dragEnterEvent(self, e):
e.accept()
def dropEvent(self, e):
position = e.pos()
self.btn.move(position)
e.setDropAction(QtCore.Qt.MoveAction)
e.accept()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our code example, we have a QtGui.QPushButton on the window.
If we click on the button with a left mouse button,
we print 'press' to the console. By right clicking and moving
the button, we perform a drag & drop operation
on the button widget.
class Button(QtGui.QPushButton):
def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent)
We create a Button class, which will derive from the QtGui.QPushButton.
We also reimplement two methods of the QtGui.QPushButton, the
mouseMoveEvent and mousePressEvent.
The mouseMoveEvent() method is the place, where the drag &
drop operation begins.
if event.buttons() != QtCore.Qt.RightButton:
return
Here we decide that we can perform drag & drop only with a right mouse button. The left mouse button is reserved for clicking on the button.
mimeData = QtCore.QMimeData() drag = QtGui.QDrag(self) drag.setMimeData(mimeData) drag.setHotSpot(event.pos() - self.rect().topLeft())
Here we create a QtGui.QDrag object.
dropAction = drag.start(QtCore.Qt.MoveAction)
The start method of the drag object starts the
drag & drop operation.
def mousePressEvent(self, e):
QtGui.QPushButton.mousePressEvent(self, e)
if e.button() == QtCore.Qt.LeftButton:
print 'press'
We print 'press' to the console if we left click on the button
with the mouse. Notice that we call mousePressEvent method
on the parent as well. Otherwise we would not see the button being pushed.
position = e.pos() self.btn.move(position)
In the dropEvent method we code what happens after we release
the mouse button and finish the drop operation. We find out the current
mouse pointer position and move a button accordingly.
e.setDropAction(QtCore.Qt.MoveAction) e.accept()
We specify the type of the drop action. In our case it is a move action.
This part of the PySide tutorial was dedicated to drag and drop.