First programs in PyQt5
last modified October 18, 2023
In this part of the PyQt5 tutorial we learn some basic functionality. The examples show a tooltip and an icon, close a window, show a message box and center a window on the desktop.
PyQt5 simple example
This is a simple example showing a small window. Yet we can do a lot with this window. We can resize it, maximise it or minimise it. This requires a lot of coding. Someone already coded this functionality. Because it is repeated in most applications, there is no need to code it over again. PyQt5 is a high level toolkit. If we would code in a lower level toolkit, the following code example could easily have hundreds of lines.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
In this example, we create a simple
window in PyQt5.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = QWidget()
w.resize(250, 150)
w.move(300, 300)
w.setWindowTitle('Simple')
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The above code example shows a small window on the screen.
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
Here we provide the necessary imports. The basic widgets are
located in PyQt5.QtWidgets module.
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
Every PyQt5 application must create an application object.
The sys.argv parameter is a list
of arguments from a command line. Python scripts can be run from
the shell. It is a way how we can control the startup of our scripts.
w = QWidget()
The QWidget widget is the base class of all user
interface objects in PyQt5. We provide the default constructor for QWidget.
The default constructor has no parent. A widget with no parent is called a window.
w.resize(250, 150)
The resize method resizes the widget.
It is 250px wide and 150px high.
w.move(300, 300)
The move method moves the widget to a position
on the screen at x=300, y=300 coordinates.
w.setWindowTitle('Simple')
We set the title of the window with setWindowTitle. The title is
shown in the titlebar.
w.show()
The show method displays the widget on the screen. A widget is
first created in memory and later shown on the screen.
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Finally, we enter the mainloop of the application. The event handling starts
from this point. The mainloop receives events from the window system and
dispatches them to the application widgets. The mainloop ends if we call the
exit
method or the main widget is destroyed. The sys.exit method
ensures a clean exit. The environment will be informed how the application
ended.
The exec_ method has an underscore. It is because
the exec is a Python keyword. And thus, exec_
was used instead.
An application icon
The application icon is a small image which is usually displayed in the top left corner of the titlebar. In the following example we show how we do it in PyQt5. We also introduce some new methods.
Some environments do not display icons in the titlebars. We need to enable them. See my answer on Stackoverflow for a solution, if you are seeing no icons.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This example shows an icon
in the titlebar of the window.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 220)
self.setWindowTitle('Icon')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('web.png'))
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The previous example was coded in a procedural style. Python programming language supports both procedural and object oriented programming styles. Programming in PyQt5 means programming in OOP.
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
...
Three important things in object oriented programming are classes,
data, and methods. Here we create a new class called Example.
The Example class inherits from the QWidget class.
This means that we call two constructors: the first one for the Example
class and the second one for the inherited class. The super
method returns the parent object of the Example class and we call its constructor.
The __init__ method is a constructor method in Python language.
self.initUI()
The creation of the GUI is delegated to the initUI method.
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 220)
self.setWindowTitle('Icon')
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon('web.png'))
All three methods have been inherited from the QWidget class.
The setGeometry does two things: it locates the window on the screen and sets
it size. The first two parameters are the x and y
positions of the window. The third is the width and the fourth is the height of the
window. In fact, it combines the resize and move methods
in one method. The last method sets the application icon. To do this, we have created a
QIcon object. The QIcon receives the path to our icon to be displayed.
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
The application and example objects are created. The main loop is started.
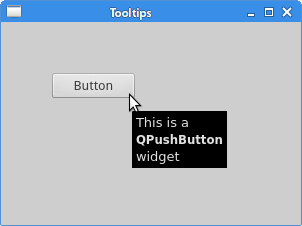
Showing a tooltip in PyQt5
We can provide a balloon help for any of our widgets.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This example shows a tooltip on
a window and a button.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QToolTip,
QPushButton, QApplication)
from PyQt5.QtGui import QFont
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
QToolTip.setFont(QFont('SansSerif', 10))
self.setToolTip('This is a <b>QWidget</b> widget')
btn = QPushButton('Button', self)
btn.setToolTip('This is a <b>QPushButton</b> widget')
btn.resize(btn.sizeHint())
btn.move(50, 50)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 200)
self.setWindowTitle('Tooltips')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In this example, we show a tooltip for two PyQt5 widgets.
QToolTip.setFont(QFont('SansSerif', 10))
This static method sets a font used to render tooltips. We use a 10pt SansSerif font.
self.setToolTip('This is a <b>QWidget</b> widget')
To create a tooltip, we call the setTooltip method. We can use
rich text formatting.
btn = QPushButton('Button', self)
btn.setToolTip('This is a <b>QPushButton</b> widget')
We create a push button widget and set a tooltip for it.
btn.resize(btn.sizeHint()) btn.move(50, 50)
The button is being resized and moved on the window. The sizeHint
method gives a recommended size for the button.
Closing a window
The obvious way to close a window is to click on the x mark on the titlebar. In the next example, we show how we can programatically close our window. We briefly touch signals and slots.
The following is the constructor of a QPushButton widget that we use
in our example.
QPushButton(string text, QWidget parent = None)
The text parameter is a text that will be displayed on the button.
The parent is a widget on which we place our button.
In our case it will be a QWidget. Widgets of an application form a hierarchy.
In this hierarchy, most widgets have their parents. Widgets without parents are toplevel windows.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This program creates a quit
button. When we press the button,
the application terminates.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QPushButton, QApplication
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
qbtn = QPushButton('Quit', self)
qbtn.clicked.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
qbtn.resize(qbtn.sizeHint())
qbtn.move(50, 50)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 250)
self.setWindowTitle('Quit button')
self.show()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In this example, we create a quit button. Upon clicking on the button, the application terminates.
qbtn = QPushButton('Quit', self)
We create a push button. The button is an instance of the QPushButton
class. The first parameter of the constructor is the label of the button.
The second parameter is the parent widget. The parent widget is the
Example widget, which is a QWidget by inheritance.
qbtn.clicked.connect(QApplication.instance().quit)
The event processing system in PyQt5 is built with the signal & slot
mechanism. If we click on the button, the signal clicked is
emitted. The slot can be a Qt slot or any Python callable.
QCoreApplication, which is retrieved with
QApplication.instance, contains the main event loop—it processes
and dispatches all events. The clicked signal is connected to the
quit method which terminates the application. The communication
is done between two objects: the sender and the receiver. The sender is the push
button, the receiver is the application object.
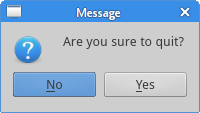
PyQt5 message box
By default, if we click on the x button on the titlebar,
the QWidget is closed. Sometimes we want to modify
this default behaviour. For example, if we have a file opened in an editor
to which we did some changes. We show a message box to confirm the action.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This program shows a confirmation
message box when we click on the close
button of the application window.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QMessageBox, QApplication
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Message box')
self.show()
def closeEvent(self, event):
reply = QMessageBox.question(self, 'Message',
"Are you sure to quit?", QMessageBox.Yes |
QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.No)
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
event.accept()
else:
event.ignore()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
If we close a QWidget, the QCloseEvent
is generated. To modify the widget behaviour we need to reimplement
the closeEvent event handler.
reply = QMessageBox.question(self, 'Message',
"Are you sure to quit?", QMessageBox.Yes |
QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.No)
We show a message box with two buttons: Yes and No. The first string appears
on the titlebar. The second string is the message text displayed by the dialog.
The third argument specifies the combination of buttons appearing in the dialog.
The last parameter is the default button. It is the button which has initially
the keyboard focus. The return value is stored in the reply variable.
if reply == QtGui.QMessageBox.Yes:
event.accept()
else:
event.ignore()
Here we test the return value. If we click the Yes button, we accept the event which leads to the closure of the widget and to the termination of the application. Otherwise we ignore the close event.
Centering window on the screen
The following script shows how we can center a window on the desktop screen.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial
This program centers a window
on the screen.
Author: Jan Bodnar
Website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QDesktopWidget, QApplication
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.resize(250, 150)
self.center()
self.setWindowTitle('Center')
self.show()
def center(self):
qr = self.frameGeometry()
cp = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()
qr.moveCenter(cp)
self.move(qr.topLeft())
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The QDesktopWidget class provides information about
the user's desktop, including the screen size.
self.center()
The code that will center the window is placed in the custom
center method.
qr = self.frameGeometry()
We get a rectangle specifying the geometry of the main window. This includes any window frame.
cp = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()
We figure out the screen resolution of our monitor. And from this resolution, we get the center point.
qr.moveCenter(cp)
Our rectangle has already its width and height. Now we set the center of the rectangle to the center of the screen. The rectangle's size is unchanged.
self.move(qr.topLeft())
We move the top-left point of the application window to the top-left point of the qr rectangle, thus centering the window on our screen.
In this part of the PyQt5 tutorial, we have created simple code examples in PyQt5.