Drawing in PyQt4
last modified October 18, 2023
Drawing is needed in painting applications when we want to change or enhance an existing widget, or if we are creating a custom widget from scratch. To do the drawing, we use the drawing API provided by the PyQt4 toolkit.
The drawing is done within the paintEvent method.
The drawing code is placed between the begin and
end methods of the QtGui.QPainter object.
It performs low-level painting on widgets and other paint devices.
Drawing text
We begin with drawing some Unicode text on the client area of a window.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we draw text in Russian azbuka.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.text = u'\u041b\u0435\u0432 \u041d\u0438\u043a\u043e\u043b\u0430\
\u0435\u0432\u0438\u0447 \u0422\u043e\u043b\u0441\u0442\u043e\u0439: \n\
\u0410\u043d\u043d\u0430 \u041a\u0430\u0440\u0435\u043d\u0438\u043d\u0430'
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('Draw text')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, event):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawText(event, qp)
qp.end()
def drawText(self, event, qp):
qp.setPen(QtGui.QColor(168, 34, 3))
qp.setFont(QtGui.QFont('Decorative', 10))
qp.drawText(event.rect(), QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter, self.text)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we draw some text in Cylliric. The text is vertically and horizontally aligned.
def paintEvent(self, event): ...
Drawing is done within the paint event.
qp = QtGui.QPainter() qp.begin(self) self.drawText(event, qp) qp.end()
The QtGui.QPainter class is responsible for all the low-level painting.
All the painting methods go between begin and end methods.
The actual painting is delegated to the drawText method.
qp.setPen(QtGui.QColor(168, 34, 3))
qp.setFont(QtGui.QFont('Decorative', 10))
Here we define a pen and a font which are used to draw the text.
qp.drawText(event.rect(), QtCore.Qt.AlignCenter, self.text)
The drawText method draws text on the window.
The rect method of the paint event returns the rectangle
that needs to be updated.
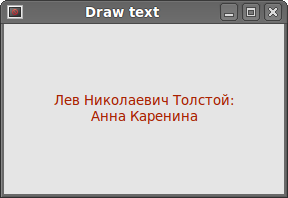
Drawing points
A point is the most simple graphics object that can be drawn. It is a small spot on the window.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In the example, we draw randomly 1000 red points
on the window.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys, random
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('Points')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawPoints(qp)
qp.end()
def drawPoints(self, qp):
qp.setPen(QtCore.Qt.red)
size = self.size()
for i in range(1000):
x = random.randint(1, size.width()-1)
y = random.randint(1, size.height()-1)
qp.drawPoint(x, y)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we draw randomly 1000 red points on the client area of the window.
qp.setPen(QtCore.Qt.red)
We set the pen to red colour. We use a predefined QtCore.Qt.red colour
constant.
size = self.size()
Each time we resize the window, a paint event is generated. We get the
current size of the window with the size method.
We use the size of the window to distribute the points all over the
client area of the window.
qp.drawPoint(x, y)
We draw the point with the drawPoint method.
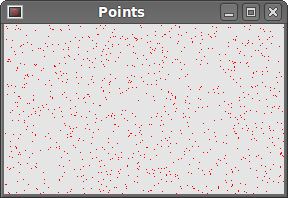
Colours
A colour is an object representing a combination of Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) intensity values. Valid RGB values are in the range from 0 to 255. We can define a colour in various ways. The most common are RGB decimal values or hexadecimal values. We can also use an RGBA value which stands for Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha. Here we add some extra information regarding transparency. Alpha value of 255 defines full opacity, 0 is for full transparency, e.g. the colour is invisible.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
This example draws three rectangles in three
different colours.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 100)
self.setWindowTitle('Colours')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawRectangles(qp)
qp.end()
def drawRectangles(self, qp):
color = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
color.setNamedColor('#d4d4d4')
qp.setPen(color)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(200, 0, 0))
qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 80, 0, 160))
qp.drawRect(130, 15, 90, 60)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(25, 0, 90, 200))
qp.drawRect(250, 15, 90, 60)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we draw 3 coloured rectangles.
color = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
color.setNamedColor('#d4d4d4')
Here we define a colour using a hexadecimal notation.
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(200, 0, 0)) qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
Here we define a brush and draw a rectangle. A brush
is an elementary graphics object which is used to draw the
background of a shape. The drawRect method accepts
four parameters. The first two are x and y values on the axis. The third and
fourth parameters are the width and height of
the rectangle. The method draws the rectangle using the current pen and brush.

QtGui.QPen
The QtGui.QPen is an elementary graphics object. It is used to draw lines,
curves and outlines of rectangles, ellipses, polygons, or other shapes.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example we draw 6 lines using
different pen styles.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 270)
self.setWindowTitle('Pen styles')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawLines(qp)
qp.end()
def drawLines(self, qp):
pen = QtGui.QPen(QtCore.Qt.black, 2, QtCore.Qt.SolidLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 40, 250, 40)
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.DashLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 80, 250, 80)
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.DashDotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 120, 250, 120)
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.DotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 160, 250, 160)
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.DashDotDotLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 200, 250, 200)
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.CustomDashLine)
pen.setDashPattern([1, 4, 5, 4])
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(20, 240, 250, 240)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we draw six lines. The lines are drawn in six different pen styles. There are five predefined pen styles. We can create also custom pen styles. The last line is drawn using a custom pen style.
pen = QtGui.QPen(QtCore.Qt.black, 2, QtCore.Qt.SolidLine)
We create a QtGui.QPen object. The colour is black. The width
is set to 2 pixels so that we can see the differences between the pen
styles. The QtCore.Qt.SolidLine is one of the predefined pen styles.
pen.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.CustomDashLine) pen.setDashPattern([1, 4, 5, 4]) qp.setPen(pen)
Here we define a custom pen style. We set a QtCore.Qt.CustomDashLine
pen style and call the setDashPattern method. The list of numbers defines a style.
There must be an even number of numbers. Odd numbers define a dash, even numbers space.
The greater the number, the greater the space or the dash. Our pattern is 1px dash, 4px
space, 5px dash, 4px space etc.
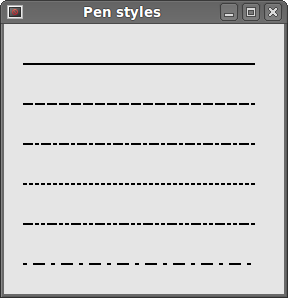
QtGui.QBrush
The QtGui.QBrush is an elementary graphics object. It is
used to paint the background of graphics shapes,
such as rectangles, ellipses, or polygons. A brush can be of three
different types: a predefined brush, a gradient, or a texture pattern.
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
This example draws 9 rectangles in different
brush styles.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 355, 280)
self.setWindowTitle('Brushes')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawBrushes(qp)
qp.end()
def drawBrushes(self, qp):
brush = QtGui.QBrush(QtCore.Qt.SolidPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.Dense1Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 15, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.Dense2Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 15, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.Dense3Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 105, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.DiagCrossPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 105, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.Dense5Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 105, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.Dense6Pattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 105, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.HorPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(10, 195, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.VerPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(130, 195, 90, 60)
brush.setStyle(QtCore.Qt.BDiagPattern)
qp.setBrush(brush)
qp.drawRect(250, 195, 90, 60)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we draw nine different rectangles.
brush = QtGui.QBrush(QtCore.Qt.SolidPattern) qp.setBrush(brush) qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
We define a brush object. We set it to the painter object and draw the
rectangle by calling the drawRect method.
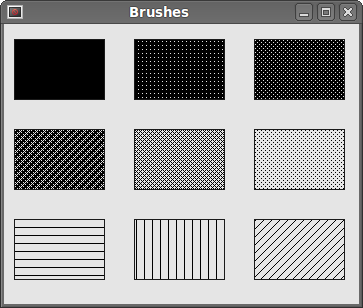
In this part of the PyQt4 tutorial, we did some basic painting.