Widgets in PyGTK
last modified October 18, 2023
In this part of the PyGTK programming tutorial, we introduce some PyGTK widgets.
Widgets are basic building blocks of a GUI application. Over the years, several widgets became a standard in all toolkits on all OS platforms. For example a button, a check box or a scroll bar. The PyGTK toolkit's philosophy is to keep the number of widgets at a minimum level. More specialised widgets are created as custom PyGTK widgets.
Label
The Label widget displays a limited amount of read-only text.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example demonstrates the Label widget
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
lyrics = """Meet you downstairs in the bar and heard
your rolled up sleeves and your skull t-shirt
You say why did you do it with him today?
and sniff me out like I was Tanqueray
cause you're my fella, my guy
hand me your stella and fly
by the time I'm out the door
you tear men down like Roger Moore
I cheated myself
like I knew I would
I told ya, I was trouble
you know that I'm no good"""
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.set_border_width(8)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.set_title("You know I'm no Good")
label = gtk.Label(lyrics)
self.add(label)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
The code example shows some lyrics on the window.
lyrics = """Meet you downstairs in the bar and heard your rolled up sleeves and your skull t-shirt ..."""
This is the text that we display.
self.set_border_width(8)
The Label is surrounded by some empty space.
label = gtk.Label(lyrics) self.add(label)
The Label widget is created and added to the window.
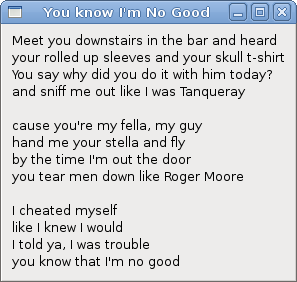
CheckButton
CheckButton is a widget that has two states: on and off.
The n state is visualised by a check mark. It is used to denote some boolean
property.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example demonstrates the CheckButton widget
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Check Button")
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.set_default_size(250, 200)
fixed = gtk.Fixed()
button = gtk.CheckButton("Show title")
button.set_active(True)
button.unset_flags(gtk.CAN_FOCUS)
button.connect("clicked", self.on_clicked)
fixed.put(button, 50, 50)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.add(fixed)
self.show_all()
def on_clicked(self, widget):
if widget.get_active():
self.set_title("Check Button")
else:
self.set_title("")
PyApp()
gtk.main()
We display a title in the titlebar of the window,
depending on the state of the CheckButton.
button = gtk.CheckButton("Show title")
CheckButton widget is created.
button.set_active(True)
The title is visible by default, so we check the check button by default.
if widget.get_active():
self.set_title("Check Button")
else:
self.set_title("")
If the CheckButton is checked
we show the title. Otherwise we put empty text in the
titlebar.
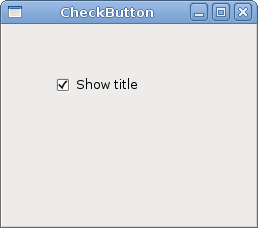
ComboBox
ComboBox is a widget that allows the
user to choose from a list of options.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example demonstrates the ComboBox widget
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("ComboBox")
self.set_default_size(250, 200)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
cb = gtk.combo_box_new_text()
cb.connect("changed", self.on_changed)
cb.append_text('Ubuntu')
cb.append_text('Mandriva')
cb.append_text('Redhat')
cb.append_text('Gentoo')
cb.append_text('Mint')
fixed = gtk.Fixed()
fixed.put(cb, 50, 30)
self.label = gtk.Label("-")
fixed.put(self.label, 50, 140)
self.add(fixed)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def on_changed(self, widget):
self.label.set_label(widget.get_active_text())
PyApp()
gtk.main()
The example shows a combo box and a label. The combo box has a list of six options. These are the names of Linux distros. The label widget shows the selected option from the combo box.
cb = gtk.combo_box_new_text()
The gtk.combo_box_new_text function is a convenience
function that constructs a new text combo box. It is a ComboBox
just displaying strings.
cb.append_text('Ubuntu')
cb.append_text('Mandriva')
cb.append_text('Redhat')
cb.append_text('Gentoo')
cb.append_text('Mint')
The ComboBox is filled with textual data.
self.label.set_label(widget.get_active_text())
Inside the on_changed method, we get the selected
text out of the combo box and set it to the label.
Image
The next example introduces the Image widget.
This widget displays pictures.
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example demonstrates the Image widget
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Red Rock")
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.set_border_width(2)
image = gtk.Image()
image.set_from_file("redrock.png")
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.add(image)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
We show the Red Rock castle in the window.
image = gtk.Image()
Image widget is created.
image.set_from_file("redrock.png")
We set a PNG image to the Image widget. The picture is
loaded from the file on the disk.

In this chapter, we showed the first pack of basic widgets of the PyGTK programming library.